REvil Members Arrested: What Put Them Behind Bars?
Written by: ceren
Written by Gokcen Tapkan
Additional Contributor Yavuz Han
Edited by Haley Williams
Russian FBI Seized 14 REvil Ransomware Group Members
Announced Friday January 14, the Russian Federal Security Bureau’s intelligence agency (FSB) seized 14 members of the long-sought REvil gang along with their stashes. REvil is an advanced ransomware group that first appeared in April 2019, and is tied to headline attacks such as Colonial Pipeline. It operates through the RAAS (ransomware as a service) model. In this model, after each attack, the revenue acquired is split among the affiliates.
The arrests were an apparent demonstration of a rare U.S. and Russia collaboration. The Russian Federal Security Bureau claims to have taken over 426 million rubles ($600,000 USD) in cash, cryptocurrency wallets, computers, and 20 automobiles at the request of the U.S. An individual allegedly linked to DarkSide and the Colonial attack was also arrested.
According to Black Kite research, the often high-profile REvil attacks accounted for 3% of the total ransomware attacks in 2021.
What do the REvil arrests signal for the future of RaaS gangs?
REvil will not be the final ransomware gang arrested as the hope of halting ransomware services grows. However, it raised concerns among the hacker community in Russia for the time being. One cybercriminal posted the following sentences [translated] after the arrests in a Russian-speaking deep-web hacker forum.

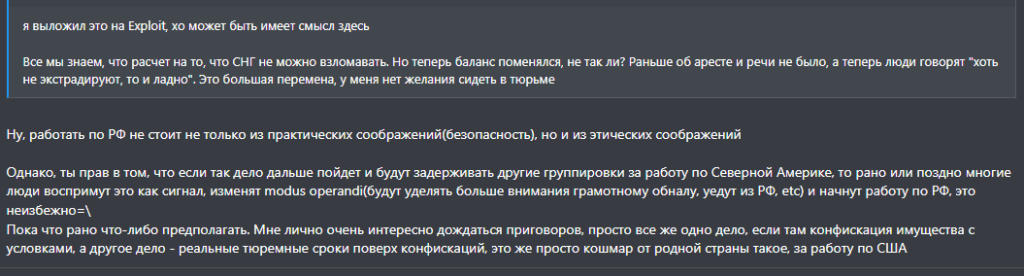
The hacker in the forum voiced concern and frustration that the recent arrests show that it is not worth working in the Russian federation any longer, for “practical and ethical reasons.” There is concern that this event will raise the alarm among the hacker community and cause shifts in methods, location, cashing and other processes.
These arrests may appear as a short-term solution to halt ransomware gangs, but most likely, gangs will stay agile and find new ways to run their operations with higher secrecy and safer monetization techniques.
What REvil attacks were most impactful in 2021?
Kaseya REvil Ransomware Attack
REvil was responsible for the famous Kaseya ransomware attack that crippled between 800 and 1500 medium-sized businesses over the 2021 Independence Day weekend.
On July 2, the IT solutions developer for MSPs and enterprise clients disclosed that Kaseya had been the target of a cyberattack. Through exploiting a series of zero-day vulnerabilities in Kaseya’s VSA software, a unified remote monitoring and management tool for handling networks and endpoints, attackers launched a supply chain ransomware attack. This was directly targeted against their MSPs and clients. This put both the MSPs and their customers at immediate risk.
One of the biggest impacts was on Coop, a line of over 800 grocery stores in Sweden that closed for one day as the attack shut down its cash registers. Black Kite dug deeper into the security posture of Kaseya at the time when the attack went public.
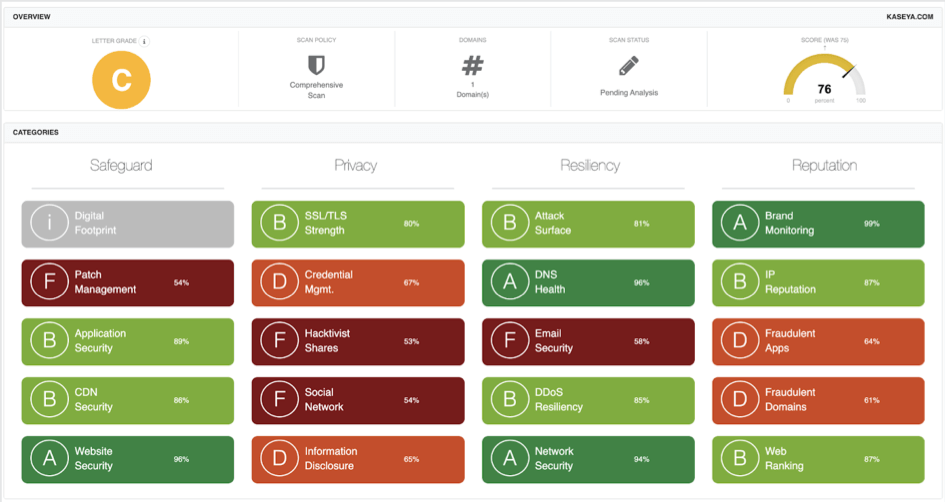
Our analysis on the 12 months preceding the attack revealed that Kaseya’s Black Kite cyber rating dropped from a ‘B’ to ‘C’ on an A-to-F rating scale (84 to 76 on a 0-100 numerical scale).
The rating mainly decreased due to poor grades for Patch Management, Credential Management, Application Security, and SSL/TLS Strength. These ratings, at that time, possibly indicated the threat actors might have accessed some of Kaseya’s systems through;
- Exploiting unpatched vulnerabilities on out-of-date systems
- Credential-stuffing attacks by using leaked credentials
- Phishing attacks via exploiting the poor email configuration
- SQL injection types of attacks on web applications
Regarding the ransom demand, Kaseya denied that it paid the ransom, announcing that it had received a decryption tool from a “third party” and was working with anti-malware experts to restore the environments of afflicted enterprises. Kaseya additionally provided the decryptor to the affected third parties upon a non-disclosure agreement.
JBS Food Faced $11 Million in Ransom
JBS, the largest beef producer globally, was hit by REvil in August. The ransomware attack forced the shutdown of all JBS beef plants located in the US. Other JBS meat packing facilities in the country faced disruption and slaughter facilities in Australia halted as a result of the attack.
Eventually, JBS confirmed an $11 million ransom was paid to the gang to prevent their data from being leaked by REvil and to expedite the reversal of disruption in the food supply chain, including restaurants that relied on JBS.
Analysis of the 2021 REvil Raas attacks
REvil, unlike some gangs, was after high-profile attacks that contained more significant returns, particularly targeting large supply chains. For instance, with the Kaseya VSA ransomware attack, the demand was $70 million, indicating a game plan of high reward.
Using Black Kite’s Ransomware Susceptibility Index™ (RSI™), our research found that REvil ransomware victims held particularly high RSI™ ratings, with an average of 0.44, indicating a substantial probability of experiencing a ransomware attack, due to various indicators such as open critical ports, endpoint security, and email security.
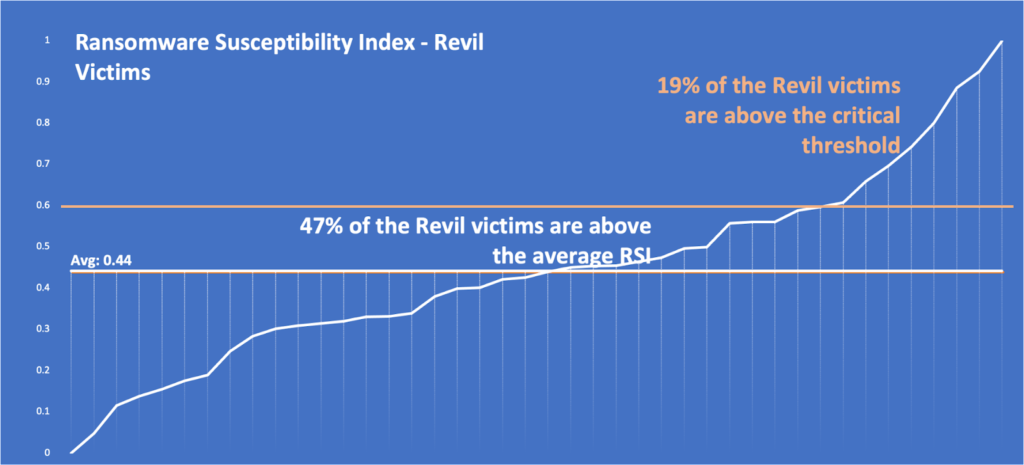
Source: Black Kite platform
The majority of REvil attacks targeted North America, with the United States receiving the most attention. Both high digitalization and cash generation in businesses as well as political incentive make U.S. organizations a primary target for Russian hackers like REvil.
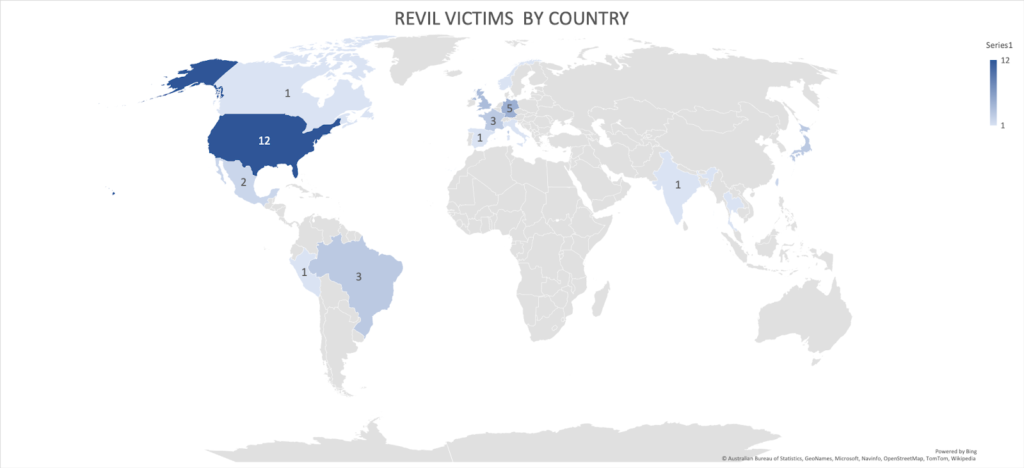
Source: Black Kite Research
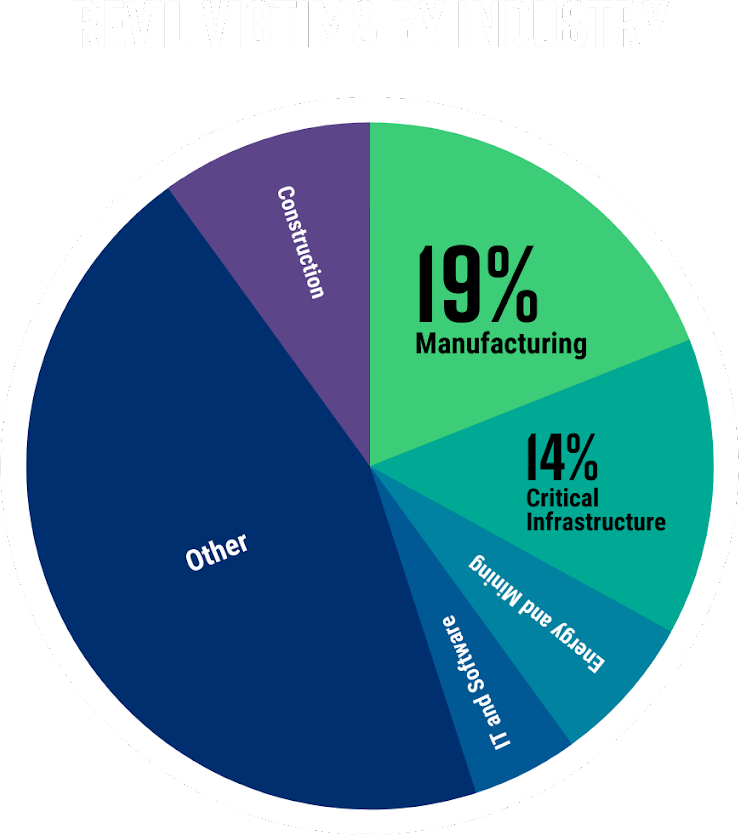
The sectors targeted by REvil have been varied and unspecific. However, it seemed the gang was primarily after high revenue manufacturing giants, regardless of industry, and critical infrastructure that cannot tolerate downtime, forcing quick payments and obedience of requirements.
If we break it down by industry, we can see that manufacturing accounted for 19% of the attacks, and critical infrastructure, including transportation, energy, and government services, accounted for 14% of the REvil attacks in 2021.
Next Steps: Recommendations and Precautions
- Make regular external backups. External means there must be no access from the main network. There should be an air gap between the enterprise and backup network.
- Security awareness training is the key to combating phishing attacks, no matter how secure your email network is. Threat actors often reach employees through other channels, such as LinkedIn or text messages.
- Use reputable antivirus software and a firewall. Give refreshers on firewall rules often, and push antivirus software updates regularly.
- Patch, patch, patch. Timely patching is the key to preventing cyber attacks, including ransomware. Companies and employees that let time linger between vulnerabilities and patches allow access opportunities for threat actors. Check out CISA’s recent advisory on “Understanding and Mitigating Russian State-Sponsored Cyber Threats to U.S. Critical Infrastructure” and see which vulnerabilities they leverage often.
See the full picture today, and start taking control of your supply chain risk.
Schedule a demoBlack Kite RSI™ Methodology
The Ransomware Susceptibility Index™ collects data from various open-source intelligence (OSINT) sources, including internet-wide scanners, hacker forums, the deep/dark web, and more to determine how susceptible a company and its third parties are to a ransomware attack.
Black Kite Research captured the Ransomware Susceptibility Index™ ratings of the REvil victims listed on the deep web. An RSI greater than 0.4 is always a red flag for a company and its stakeholders. Black Kite Research foresees a high level of confidence in the timeliness of RSI scores since ransomware attacks do not involve a wide window for transfer of payment.

