FOCUS FRIDAY: TPRM Insights on FortiGate, QNAP, Mongoose, and W3 Total Cache Vulnerabilities with Black Kite’s FocusTags™
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, the rapid emergence of critical vulnerabilities demands an agile and informed approach to Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM). This week’s Focus Friday blog highlights high-profile incidents involving vulnerabilities in FortiGate firewalls, QNAP NAS systems, Mongoose, and the W3 Total Cache WordPress plugin. Each of these vulnerabilities poses unique challenges, from authentication bypasses enabling unauthorized access to database manipulation and SSRF attacks.
Leveraging Black Kite’s FocusTags™, we delve into the impact of these vulnerabilities from a TPRM perspective. This article offers detailed insights into the risks, remediation strategies, and questions TPRM professionals should be asking vendors to protect their ecosystems against potential breaches.
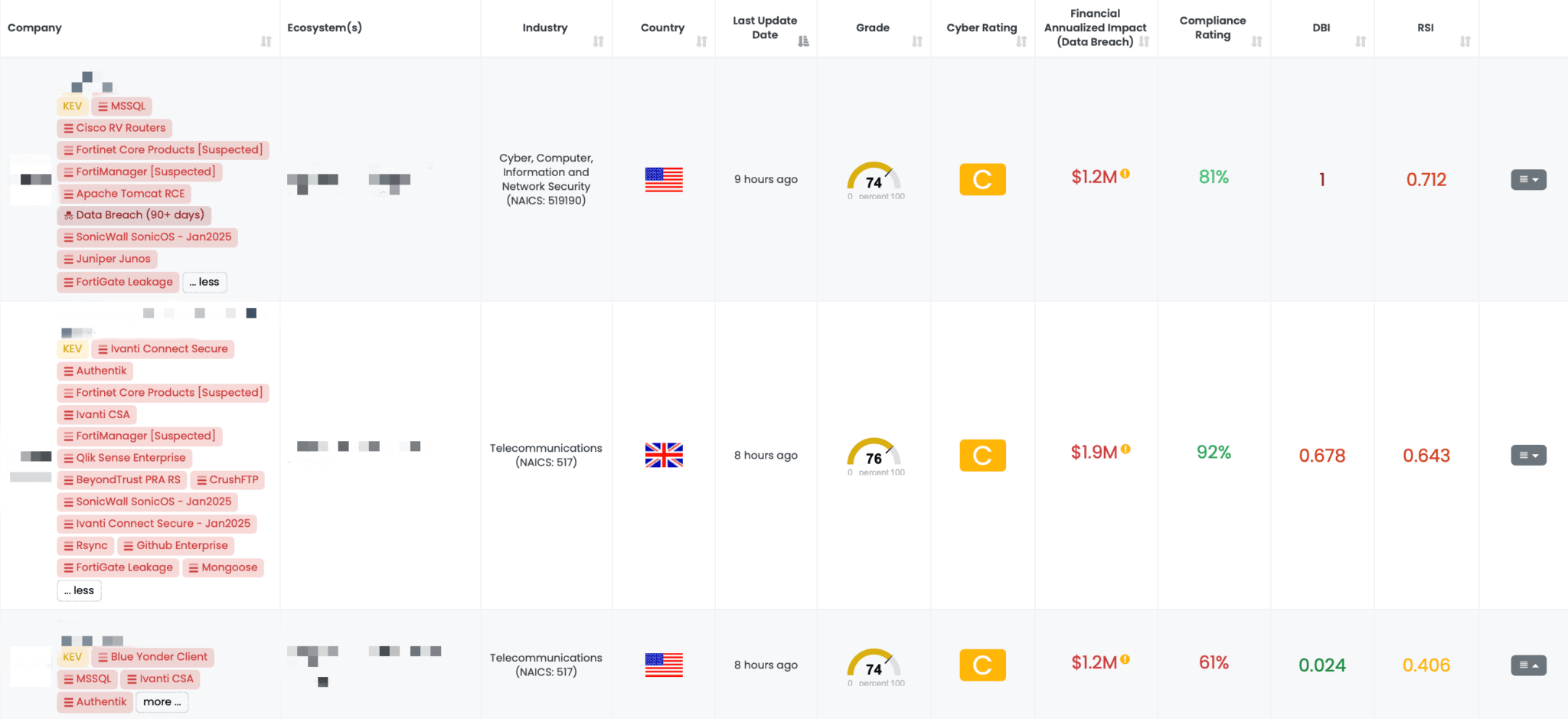
Filtered view of companies with FortiGate Leakage FocusTag™ on the Black Kite platform.
CVE-2022-40684: FortiGate Authentication Bypass Vulnerability
What is CVE-2022-40684?
CVE-2022-40684 is a critical authentication bypass vulnerability affecting Fortinet’s FortiOS, FortiProxy, and FortiSwitchManager products. This flaw allows unauthenticated attackers to perform administrative operations via specially crafted HTTP or HTTPS requests. The vulnerability has a CVSS score of 9.8, indicating its critical severity, and an EPSS score of 97.26%, reflecting the significant likelihood of exploitation. First identified in October 2022, this vulnerability has been actively exploited in the wild, with reports of threat actors leveraging it to download device configurations and add unauthorized super_admin accounts. Notably, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added CVE-2022-40684 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog on October 11, 2022.
As part of Black Kite Research & Intelligence Team (BRITE), we have proactively addressed the exposure of configuration files, IP addresses, and VPN credentials belonging to over 15,000 FortiGate devices identified and analyzed on the dark web.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Be Concerned About CVE-2022-40684?
Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) professionals should be particularly vigilant regarding CVE-2022-40684 due to its potential impact on network security. The recent leak of configuration files and VPN credentials for over 15,000 FortiGate devices underscores the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive systems. If a vendor utilizes vulnerable FortiGate products, their compromised systems could serve as entry points for attackers, leading to data breaches and disruptions that may cascade to connected organizations. Given the critical role of firewalls in protecting network perimeters, any compromise can have far-reaching consequences.
What Questions Should TPRM Professionals Ask Vendors Regarding CVE-2022-40684?
To assess and mitigate risks associated with this vulnerability, TPRM professionals should inquire:
- Have you updated all instances of FortiOS, FortiProxy, and FortiSwitchManager products to the latest firmware versions where CVE-2022-40684 has been patched?
- Can you confirm if you have implemented IP restrictions, enhanced network activity monitoring, and deactivated the HTTP/HTTPS administrative interface as recommended in the advisory to mitigate the risk of CVE-2022-40684?
- Have you reset all VPN and administrative credentials, especially those previously configured, and reviewed your firewall rules and configurations to ensure they align with current security best practices following the FortiGate firewall configuration leak?
- Have you verified if your FortiGate devices are among the compromised by reviewing the leaked data and taken necessary actions to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive systems.
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors
Vendors using affected Fortinet products should:
- Update Firmware: Upgrade to the latest firmware versions that address CVE-2022-40684.
- Change Credentials: Reset all VPN and administrative credentials, especially those previously configured.
- Review Configurations: Assess and modify firewall rules and configurations to align with current security best practices.
- Disable Administrative Interface: Deactivate the HTTP/HTTPS administrative interface to reduce the attack surface.
- Implement IP Restrictions: Limit access to the administrative interface by allowing only trusted IP addresses.
- Monitor Network Activity: Enhance monitoring to detect any unauthorized access or anomalies.
How Can TPRM Professionals Leverage Black Kite for This Vulnerability?
Black Kite has proactively addressed this issue by publishing the “FortiGate Leakage” FocusTag™ on January 17, 2025. This tag enables TPRM professionals to identify vendors potentially affected by the FortiGate data leak. By providing detailed asset information, including IP addresses and subdomains associated with the compromised devices, Black Kite empowers organizations to assess and mitigate risks efficiently. This actionable intelligence allows for targeted inquiries and remediation efforts, ensuring a robust third-party risk management strategy.
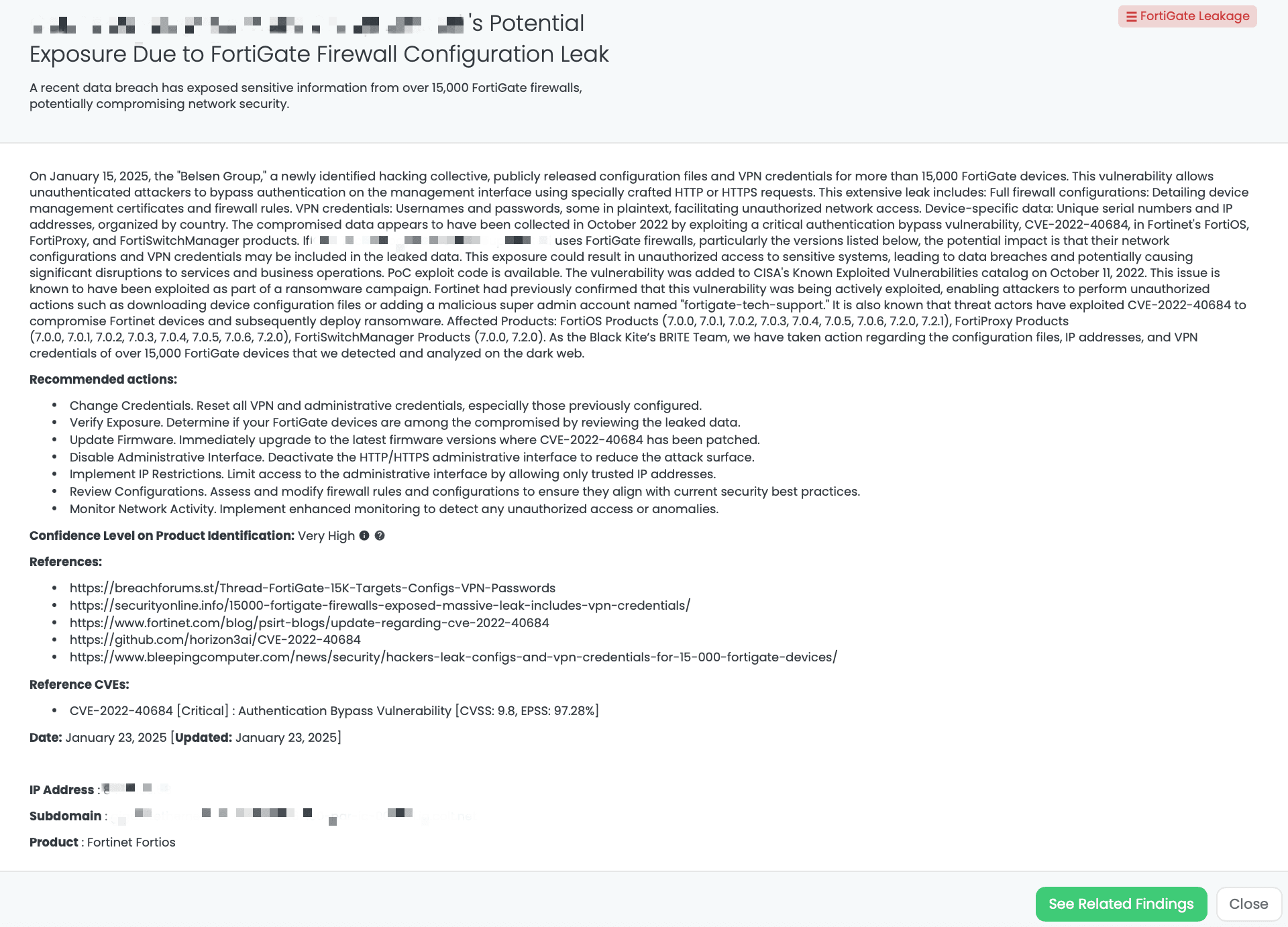
Black Kite’s FortiGate Leakage FocusTagTM details critical insights on the event for TPRM professionals.
CVE-2024-53691 and CVE-2023-39298 in QNAP QTS and QuTS Hero
What are CVE-2024-53691 and CVE-2023-39298?
CVE-2024-53691 is a link following a vulnerability in QNAP’s QTS and QuTS hero operating systems. It allows remote attackers with user access to traverse the file system to unintended locations, potentially leading to unauthorized access to sensitive files and system compromise. This vulnerability has a CVSS score of 8.7.
CVE-2023-39298 is a missing authorization vulnerability affecting several QNAP operating system versions. It permits local authenticated users to access data or perform actions they should not be allowed to via unspecified vectors. This vulnerability has a CVSS score of 7.8. As of January 23, 2025, neither vulnerability has been added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Be Concerned About These Vulnerabilities?
QNAP NAS devices are widely used for storing and managing critical business data. Exploitation of these vulnerabilities could lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and potential system compromises. For Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) professionals, it’s crucial to assess whether vendors utilize vulnerable QNAP systems, as a compromise could indirectly affect your organization’s data integrity and security.
What Questions Should TPRM Professionals Ask Vendors Regarding These Vulnerabilities?
To evaluate the risk associated with these vulnerabilities, TPRM professionals should inquire:
- Can you confirm if you have upgraded all instances of QNAP QTS and QuTS hero to versions QTS 5.2.0.2802 build 20240620 and QuTS hero h5.2.0.2802 build 20240620 or later to mitigate the risk of CVE-2024-53691 and CVE-2023-39298?
- Have you implemented the recommended actions such as monitoring system logs, applying security patches promptly, implementing MFA, and restricting network access to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access due to the link following vulnerability in QNAP QTS and QuTS hero operating systems?
- Can you confirm if you have taken measures to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive files and potential system compromise due to the link following vulnerability (CVE-2024-53691) in QNAP QTS and QuTS hero operating systems?
- Have you taken any additional steps to protect your QNAP devices from data theft, ransomware attacks, or malware deployment that could result from exploiting the vulnerabilities CVE-2024-53691 and CVE-2023-39298?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors
Vendors utilizing affected QNAP systems should:
- Update Firmware: Upgrade to QTS 5.2.0.2802 build 20240620 or QuTS hero h5.2.0.2802 build 20240620 or later.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enhance account security to prevent unauthorized access.
- Restrict Network Access: Configure firewalls and network settings to allow only trusted IP addresses access to NAS devices.
- Monitor System Logs: Regularly review logs for unusual activity indicating attempted exploitation.
- Apply Security Patches Promptly: Ensure all security patches are applied as soon as they become available.
How Can TPRM Professionals Leverage Black Kite for These Vulnerabilities?
Black Kite released the “QNAP QTS – Jan2025” FocusTag™ on January 23, 2025, to help organizations identify vendors potentially affected by these vulnerabilities. This tag provides detailed information, including the specific assets (IP addresses and subdomains) associated with vulnerable QNAP systems within a vendor’s infrastructure. By utilizing this intelligence, TPRM professionals can prioritize assessments and remediation efforts, ensuring that vendors have addressed these critical vulnerabilities.
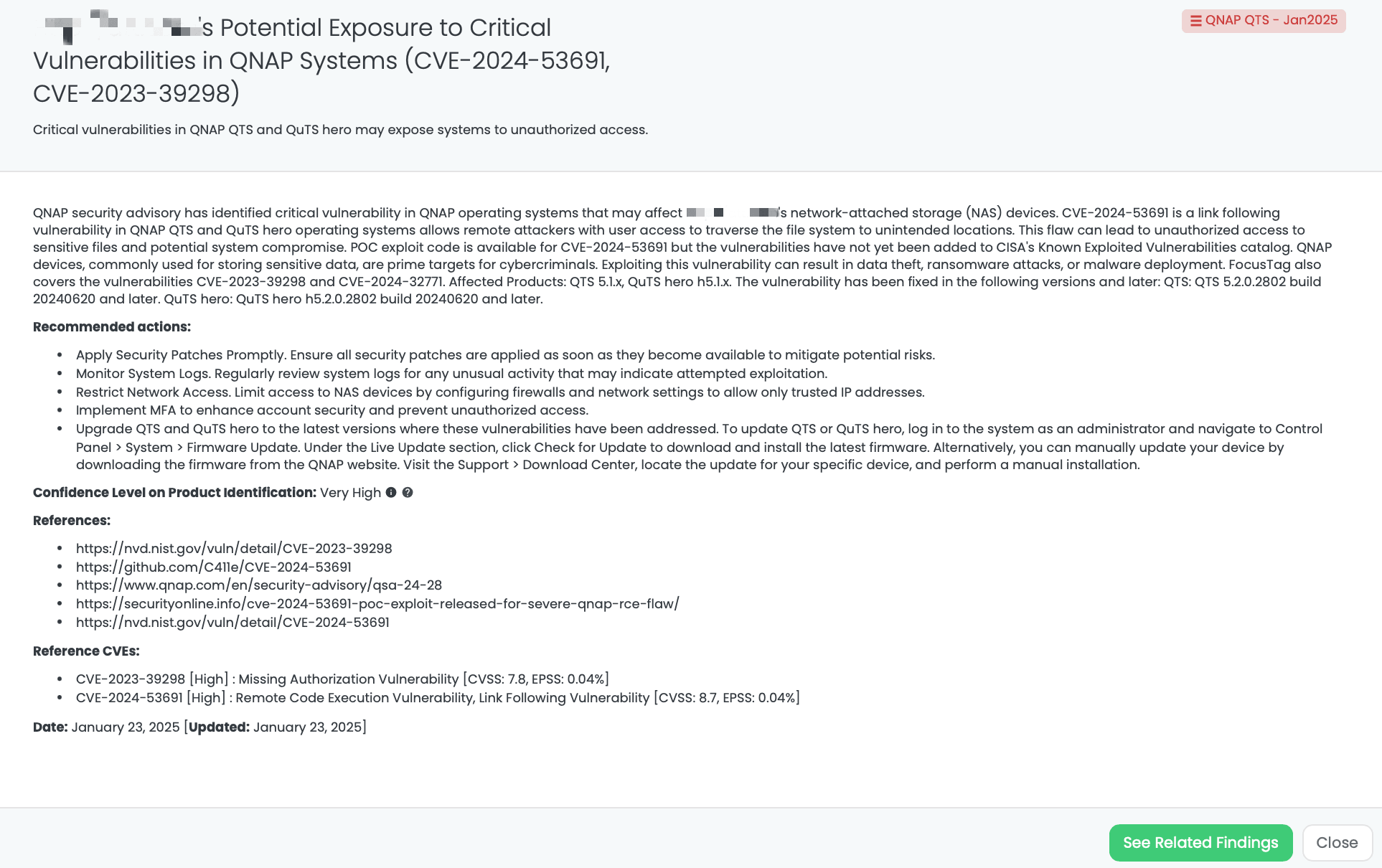
Black Kite’s QNAP QTS – Jan2025 FocusTagTM details critical insights on the event for TPRM professionals.
CVE-2025-23061 in Mongoose
Mongoose is specifically an Object Data Modeling (ODM) library designed for Node.js, enabling easy interaction with MongoDB databases. It simplifies the management, validation, and modeling of data in MongoDB, providing developers with a more structured and secure working environment.
What is CVE-2025-23061?
CVE-2025-23061 is a critical code injection vulnerability affecting Mongoose, a MongoDB object modeling tool widely used for Node.js and Deno applications. It has a CVSS score of 9.0, emphasizing its severity, while the EPSS score is 0.05%, suggesting a lower probability of exploitation at present. This vulnerability arises from improper handling of nested $where filters used with the populate() function’s match option, enabling attackers to manipulate search queries and access sensitive data.
This flaw is linked to an incomplete fix for CVE-2024-53900, another critical issue involving the $where operator’s improper handling. The vulnerability impacts Mongoose versions prior to 8.9.5. Although PoC exploit code is unavailable and it has not been added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog, its potential impact is significant due to Mongoose’s wide adoption, with over 2.7 million weekly downloads.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Be Concerned About CVE-2025-23061?
TPRM professionals should consider this vulnerability a high-priority concern due to Mongoose’s extensive use in applications that store sensitive data. If a vendor utilizes an unpatched version of Mongoose, their database integrity could be compromised, resulting in data manipulation, unauthorized access, or even larger breaches affecting downstream partners and customers. The prevalence of Mongoose as a dependency in critical systems underscores the potential ripple effect of an exploit.
What Questions Should TPRM Professionals Ask Vendors Regarding CVE-2025-23061?
To evaluate vendor risk associated with this vulnerability, consider asking:
- Have you upgraded Mongoose to version 8.9.5 or later to mitigate the risk of CVE-2025-23061 and the previously related CVE-2024-53900?
- Can you confirm if you have reviewed your application’s use of the populate() function and $where filters to ensure no unintended exposure exists, as recommended in the advisory?
- Have you implemented robust input validation and sanitization measures to prevent potential search injection attacks related to the Mongoose vulnerability?
- Are you regularly auditing and updating all dependencies to incorporate the latest security patches, specifically those related to Mongoose and MongoDB object modeling tools?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors
Vendors using Mongoose should:
- Update Mongoose: Upgrade to version 8.9.5 or later to address the vulnerability.
- Audit Codebase: Review the usage of $where filters and the populate() function to identify and mitigate potential exposure.
- Implement Input Validation: Enforce robust validation and sanitization mechanisms for all database queries.
- Monitor Dependencies: Regularly review and update dependencies to ensure all security patches are applied promptly.
How Can TPRM Professionals Leverage Black Kite for This Vulnerability?
Black Kite published the “Mongoose” FocusTag™ on January 22, 2025, to help organizations identify vendors potentially affected by this vulnerability. This tag provides high-confidence identification of systems using vulnerable Mongoose versions, offering actionable insights into affected assets, including IP addresses and subdomains. TPRM professionals can leverage this intelligence to prioritize their vendor risk assessments and ensure remediation efforts are effectively targeted.
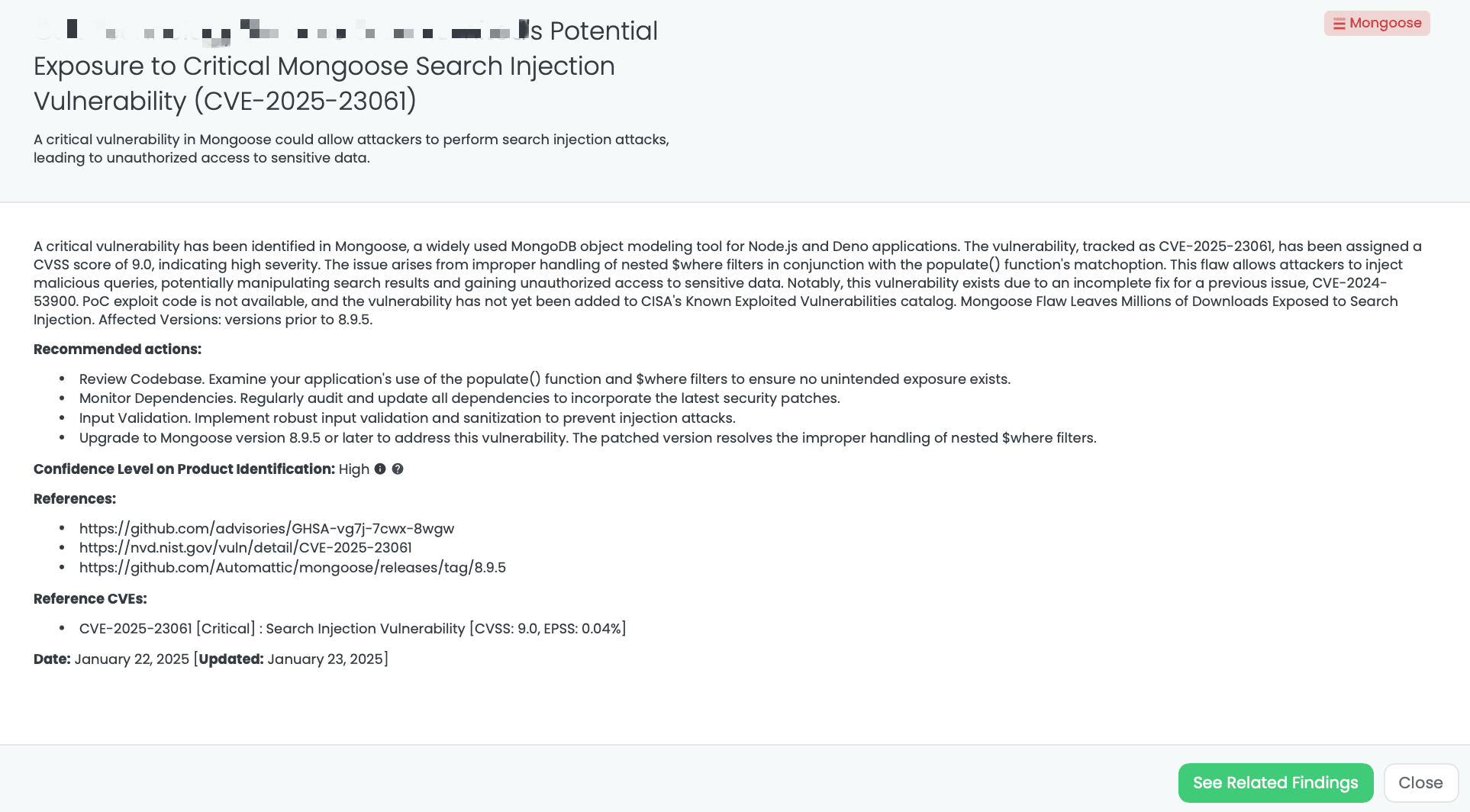
Black Kite’s Mongoose FocusTagTM details critical insights on the event for TPRM professionals.
CVE-2024-12365 in W3 Total Cache Plugin
W3 Total Cache (W3TC) is a well-known and powerful caching and performance optimization plugin designed for WordPress websites. This plugin enhances website speed, reduces loading times, and improves the overall user experience. It is particularly effective in delivering significant performance improvements for high-traffic websites.
What is CVE-2024-12365?
CVE-2024-12365 is a high-severity missing authorization vulnerability in the W3 Total Cache plugin for WordPress, affecting versions up to and including 2.8.1. With a CVSS score of 8.5 and an EPSS score of 0.09%, this vulnerability allows authenticated users with Subscriber-level access to exploit the is_w3tc_admin_page function to retrieve the plugin’s nonce value. Attackers can leverage this to perform unauthorized actions, potentially leading to information disclosure and server-side request forgery (SSRF).
Exploitation of this flaw could allow attackers to query internal services, including metadata on cloud-based applications, and consume service plan limits. While no PoC exploit code is currently available, more than a million WordPress sites using this plugin are at risk. As of January 22, 2025, this vulnerability has not been added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Be Concerned About CVE-2024-12365?
Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) professionals should be highly attentive to this vulnerability due to its potential to expose sensitive internal data and compromise WordPress-based websites. Many businesses rely on WordPress as their primary web platform, and vulnerabilities in widely-used plugins like W3 Total Cache can create significant risks.
If a vendor’s website is compromised through this flaw, it may lead to:
- Data breaches involving sensitive business or customer information.
- Unintended exposure of internal application data through SSRF attacks.
- Loss of trust and credibility due to website exploitation.
Given the widespread use of WordPress and this specific plugin, the impact of unpatched systems can extend across interconnected organizations and their customers.
What Questions Should TPRM Professionals Ask Vendors Regarding CVE-2024-12365?
To evaluate vendor risk, TPRM professionals can ask the following targeted questions:
- Can you confirm if you have updated the W3 Total Cache plugin for WordPress to version 2.8.2 or later, which addresses the CVE-2024-12365 vulnerability?
- Have you implemented any additional security measures to monitor for unauthorized access or unusual behavior on your WordPress sites that could indicate exploitation attempts related to the CVE-2024-12365 vulnerability?
- Have you conducted an audit of user roles and permissions to ensure that only necessary privileges are granted, minimizing potential exploitation by lower-level users as recommended in the advisory for the CVE-2024-12365 vulnerability?
- Can you confirm if you have taken any steps to mitigate the risk of server-side request forgery, such as implementing security best practices or updating the W3 Total Cache plugin, in response to the CVE-2024-12365 vulnerability?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors
Vendors using the W3 Total Cache plugin should take the following steps:
- Update the Plugin: Upgrade to version 2.8.2 or newer, where the vulnerability has been fixed.
- Audit User Permissions: Review and minimize privileges for users, ensuring Subscriber-level accounts have limited access.
- Monitor Activity: Regularly review website activity logs for unusual or unauthorized behavior.
- Enforce Security Best Practices: Maintain strong security protocols for WordPress installations, including strong passwords, regular plugin updates, and security plugins for intrusion detection.
How Can TPRM Professionals Leverage Black Kite for This Vulnerability?
Black Kite released the “W3 Total Cache” FocusTag™ on January 22, 2025, to help organizations identify vendors potentially impacted by this vulnerability. By providing very high-confidence information, such as asset-level details (e.g., IP addresses and subdomains), Black Kite enables TPRM professionals to quickly assess and mitigate risks. This FocusTag™ is instrumental in narrowing down affected vendors and ensuring targeted remediation efforts.
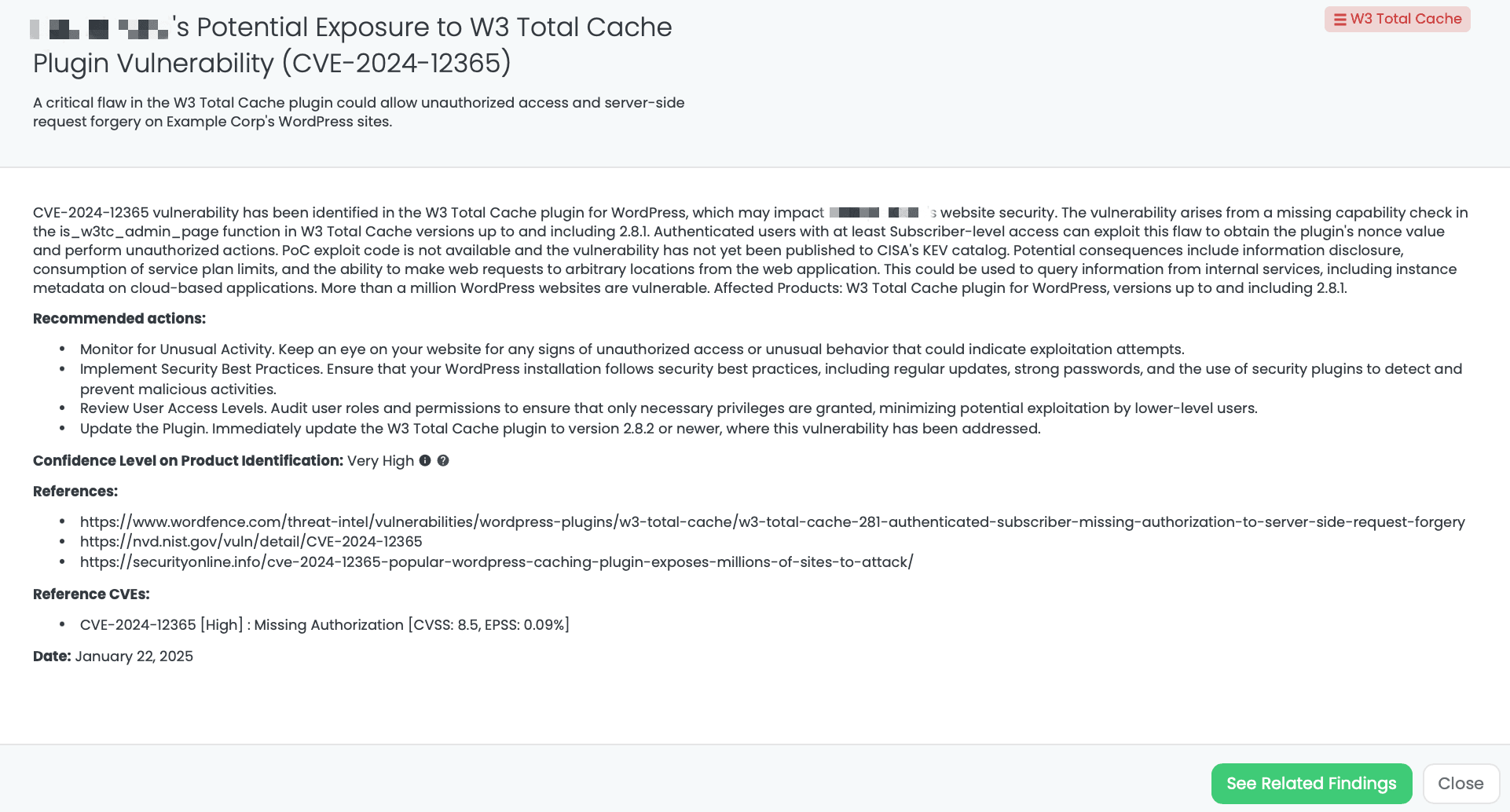
Black Kite’s W3 Total Cache FocusTagTM details critical insights on the event for TPRM professionals.
Enhancing TPRM Strategies with Black Kite’s FocusTags™
Black Kite’s FocusTags™ are transformative tools designed to empower Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) professionals with actionable insights in the face of an ever-evolving threat landscape. With this week’s vulnerabilities spanning multiple platforms and industries, the value of these FocusTags™ becomes especially apparent:
- Real-Time Threat Awareness: Instantly pinpoint vendors impacted by vulnerabilities like those in FortiGate firewalls, QNAP NAS systems, Mongoose, and the W3 Total Cache plugin, enabling rapid and targeted action.
- Prioritized Risk Management: Evaluate risks based on the criticality of the vulnerabilities and the vendor’s importance, allowing for efficient allocation of resources to mitigate threats.
- Tailored Vendor Engagement: Facilitate meaningful conversations with vendors, focusing on their exposure to vulnerabilities and the specific actions they’ve taken to address them.
- Enhanced Cybersecurity Posture: Gain a comprehensive view of the threat landscape, supporting the development of robust strategies to defend against future risks.
By translating complex cybersecurity data into practical intelligence, Black Kite’s FocusTags™ help TPRM professionals navigate the complexities of vendor risk management with precision and confidence. These tools are essential for maintaining resilience in today’s fast-paced digital environment, where proactive risk mitigation can mean the difference between security and compromise.
About Focus Friday
Every week, we delve into the realms of critical vulnerabilities and their implications from a Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) perspective. This series is dedicated to shedding light on pressing cybersecurity threats, offering in-depth analyses, and providing actionable insights.
FocusTagsTM in the Last 30 Days:
- FortiGate Leakage: CVE-2022-40684, Authentication Bypass Vulnerability, Leaked Configurations and VPN Credentials for 15,000 FortiGate Devices.
- QNAP QTS – Jan2025: CVE-2024-53691, CVE-2023-39298, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability, Link Following Vulnerability, Missing Authorization Vulnerability in QNAP QTS.
- Mongoose: CVE-2025-23061, Search Injection Vulnerability in Mongoose.
- W3 Total Cache: CVE-2024-12365, Missing Authorization Vulnerability in WordPress’ W3 Total Cache Plugin.
- Juniper Junos: CVE-2025-21598, Out-of-bounds Read Vulnerability in Juniper’s Junos.
- Rsync: CVE-2024-12084, CVE-2024-12085, CVE-2024-12086, CVE-2024-12087, CVE-2024-12088, CVE-2024-12747, Heap-Buffer-Overflow Vulnerability, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability, Information Leak Vulnerability, File Leak Vulnerability, Path Traversal Vulnerability, Race Condition Vulnerability, Privilege Escalation Vulnerability in Rsync.
- SimpleHelp: CVE-2024-57727, CVE-2024-57728, CVE-2024-57726, Unauthenticated Path Traversal Vulnerability, Arbitrary File Upload Vulnerability, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability, Privilege Escalation Vulnerability in SimpleHelp.
- SonicWall SonicOS – Jan2025: CVE-2024-40762, CVE-2024-53704, CVE-2024-53706, CVE-2024-53705, Use of Cryptographically Weak Pseudo-Random Number Generator (PRNG), Authentication Bypass Vulnerability, Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) Vulnerability, and Local Privilege Escalation Vulnerability in SonicWall’ SonicOS SSLVPN, SSH Management, and Gen7 Cloud NSv SSH Config Function.
- Ivanti Connect Secure – Jan2025: CVE-2025-0282, CVE-2025-0283, Stack-Based Buffer Overflow Vulnerability, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability, Privilege Escalation Vulnerability in Ivanti Connect Secure, Policy Secure, and Ivanti Neurons for ZTA gateways.
- Progress WhatsUp Gold: CVE-2024-12108, CVE-2024-12106, CVE-2024-12105, Authentication Bypass by Spoofing Vulnerability, Missing Authentication for Critical Function, and Path Traversal Vulnerability in Progress WhatsUp Gold.
- GoCD: CVE-2024-56320, Improper Authorization Vulnerability in GoCD.
- Apache Tomcat RCE: CVE-2024-56337, CVE-2024-50379, Time-of-check Time-of-use (TOCTOU) Race Condition Vulnerability, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Apache Tomcat.
- CrushFTP: CVE-2024-53552, Account Takeover Vulnerability in CrushFTP.
- Gogs Server: CVE-2024-55947, CVE-2024-54148, Path Traversal Vulnerability in Gogs Server.
- BeyondTrust PRA RS: CVE-2024-12356, Command Injection Vulnerability in BeyondTrust’s Privileged Remote Access (PRA), Remote Support (RS).
- Ivanti Cloud Services Application: CVE-2024-11639, CVE-2024-11772, CVE-2024-11772, Authentication Bypass Vulnerability Command Injection Vulnerability, and RCE Vulnerability SQLi Vulnerability in Ivanti Cloud Services Application.
- Cleo File Transfer: CVE-2024-50623, CVE-2024-55956, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability, Unrestricted File Upload and Download Vulnerability in Cleo Harmony, VLTrader, LexiCom.
References
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2022-40684
https://breachforums.st/Thread-FortiGate-15K-Targets-Configs-VPN-Passwords
https://securityonline.info/15000-fortigate-firewalls-exposed-massive-leak-includes-vpn-credentials
https://www.fortinet.com/blog/psirt-blogs/update-regarding-cve-2022-40684
https://github.com/horizon3ai/CVE-2022-40684
https://www.qnap.com/en/security-advisory/qsa-24-28
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-53691
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2023-39298
https://securityonline.info/cve-2024-53691-poc-exploit-released-for-severe-qnap-rce-flaw
https://github.com/C411e/CVE-2024-53691
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-23061
https://github.com/advisories/GHSA-vg7j-7cwx-8wgw
https://github.com/Automattic/mongoose/releases/tag/8.9.5
CVE-2025-2306 (CVSS 9.0): Mongoose Flaw Leaves Millions of Downloads Exposed to Search Injection