Atlassian Confluence RCE Vulnerability on the Supply Chain
Written by: ceren
Written by Ferhat Dikbiyik
Additional Contributor Yavuz Han
Edited by Haley Williams
On June 2, 2022, Atlassian released a security advisory to Confluence Server and Data Center. The critical 0-day vulnerability on Atlassian Confluence Server and Data Center allows unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE), allowing an attacker to fully take over the target application. Atlassian states that there are known exploits of this vulnerability.
Confluence, a web-based team collaboration platform for managing workspaces and projects, is widely used by organizations. Like other RCE vulnerabilities, this vulnerability (tracked as CVE-2022-26134) creates concerns for large organizations in Confluence’s supply chain. A vendor susceptible to the Confluence RCE vulnerability might allow a threat actor to find a way to access such organizations. Understanding the nature of the vulnerability is essential to discovering the vendor who might have it.
What is the CVE-2022-26134 Vulnerability?
Cybersecurity company Volexity initially discovered this 0-day vulnerability. According to Volexity, this vulnerability was found over the 2022 Memorial Day weekend in the United States. After discovering and verifying the vulnerability, Volexity contacted Atlassian to provide full details on May 31, 2022.
CVE-2022-26134 stated that this is a remote code execution vulnerability in the Atlassian Confluence Server and Data Center. The company reported the vulnerability with a CVSS score of 10.0 out of 10.0 (maximum criticality).
During their investigation, Veloxity Research Team discovered bash shells launched by Confluence. The team found that the web server process and its child processes created by the exploit were all running as the root (full privileges) user and group. Attackers with access to the shell were able to have complete control over the Confluence Server.
If attackers successfully exploit Confluence Server systems, they can deploy malicious codes remotely. For instance, in one exploit, the attackers deployed an in-memory copy of the BEHINDER implant that provides powerful capabilities to attackers, including memory-only web shells and built-in support for interaction with Meterpreter and Cobalt Strike.
The exploit in the wild
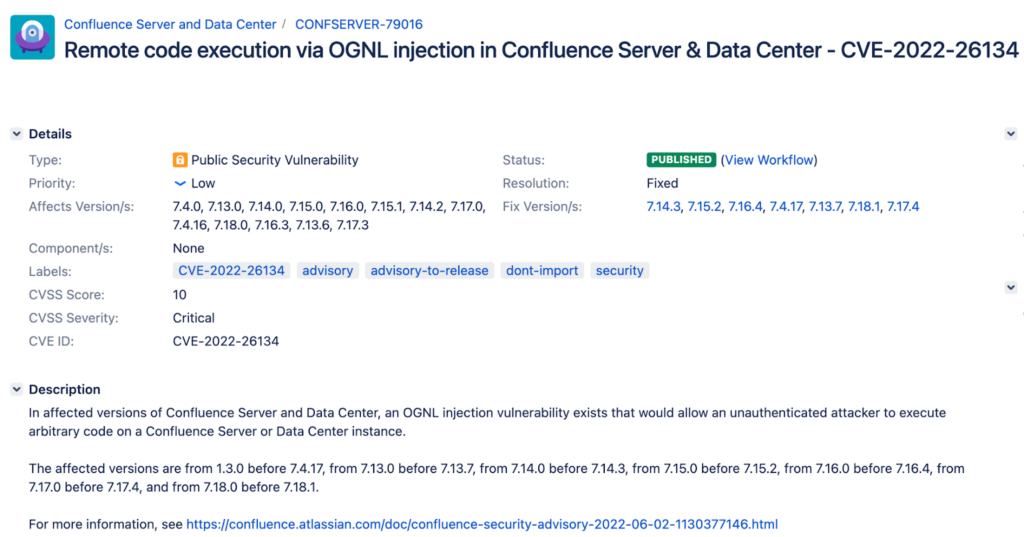
GreyNoise: over 1017 unique IP addresses attempting to exploit the Atlassian Confluence Server
According to GreyNoise, As of 7-Jun-22, over 1017 unique IP addresses attempted to exploit the Atlassian Confluence Server OGNL Injection Attempt vulnerability, CVE-2022-26134.
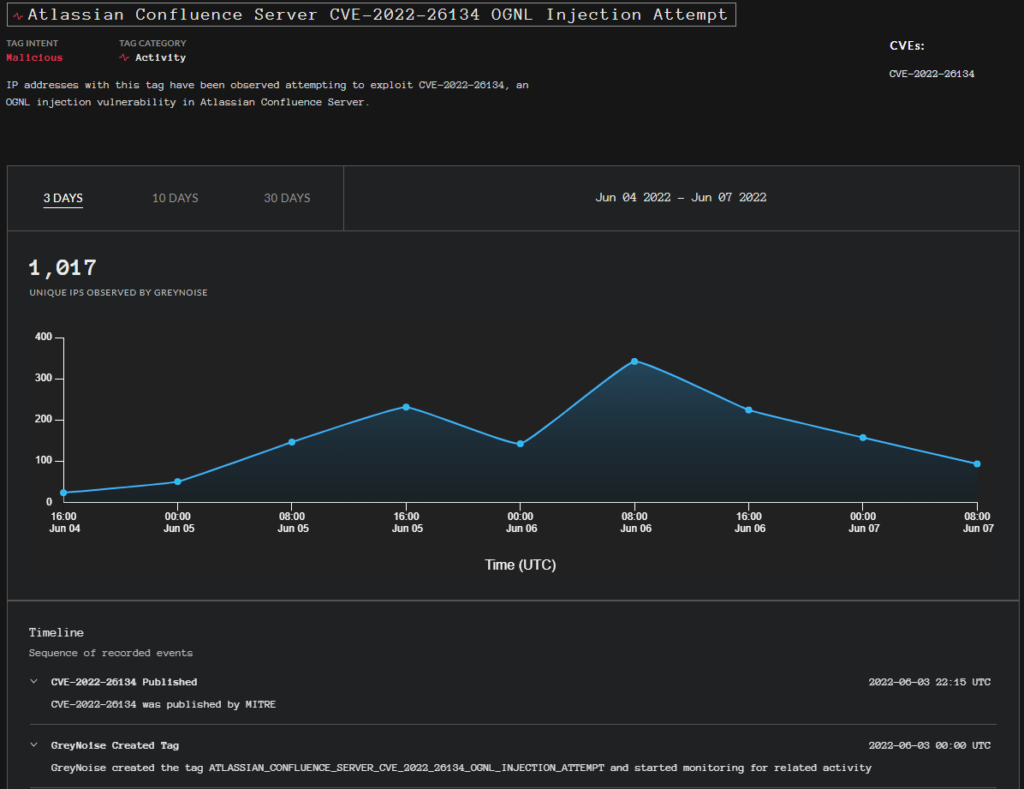
Shodan: 8305 unique IP addresses contain this vulnerability
According to Shodan’s current results (as of June 7), 8305 unique IP addresses contain this vulnerability worldwide, a quarter being located in the U.S.
The affected Atlassian versions
According to Atlassian’s official description, versions impacted by CVE-2022-26134 in Confluence Server and Confluence Data Center are:
- All supported versions of Confluence Server and Data Center are affected.
- Confluence Server and Data Center versions after 1.3.0 are affected.
The effect on the digital supply chain
Atlassian is the immediate software vendor that organizations should keep an eye on. With its high number of vulnerabilities with the exploits in the wild, Black Kite identified Atlassian as a High Impact–High Probability vendor with its Vulnerable Software Identifier (VSI) Module.
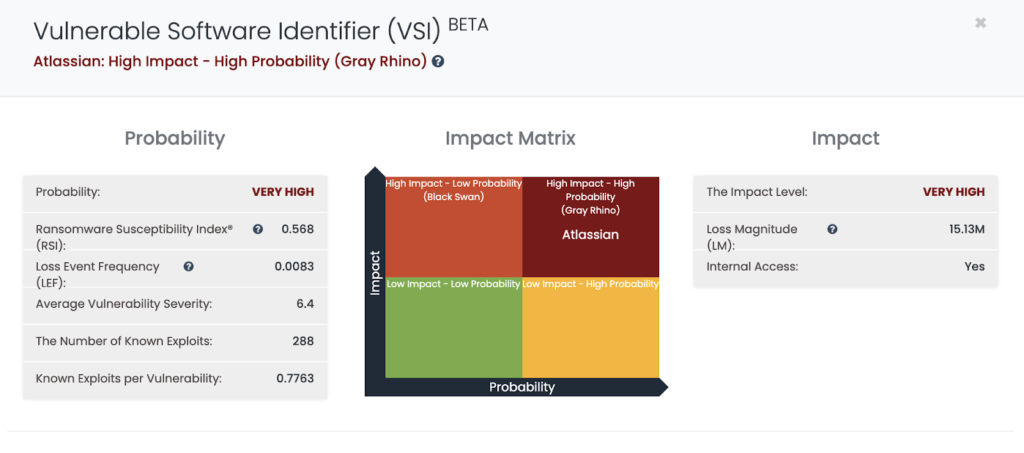
An agile patching cadence is a must to successfully protect your organization for software like Atlassian. However, threat actors may target your vendors using affected versions of Atlassian Confluence in your supply chain, by exploiting this RCE vulnerability. Further remediation steps for the vulnerability are listed in the last section of this article.
How to detect vendors that use Atlassian Confluence
Organizations usually send notifications to all vendors about a critical vulnerability and ask them to remediate it. However, without knowing which vendor might have the vulnerability, it is a very difficult process to manage, especially with hundreds of vendors. Without pointing the right asset to the vendor, vendors might respond too late. With a vulnerability such as this, time is of the essence.
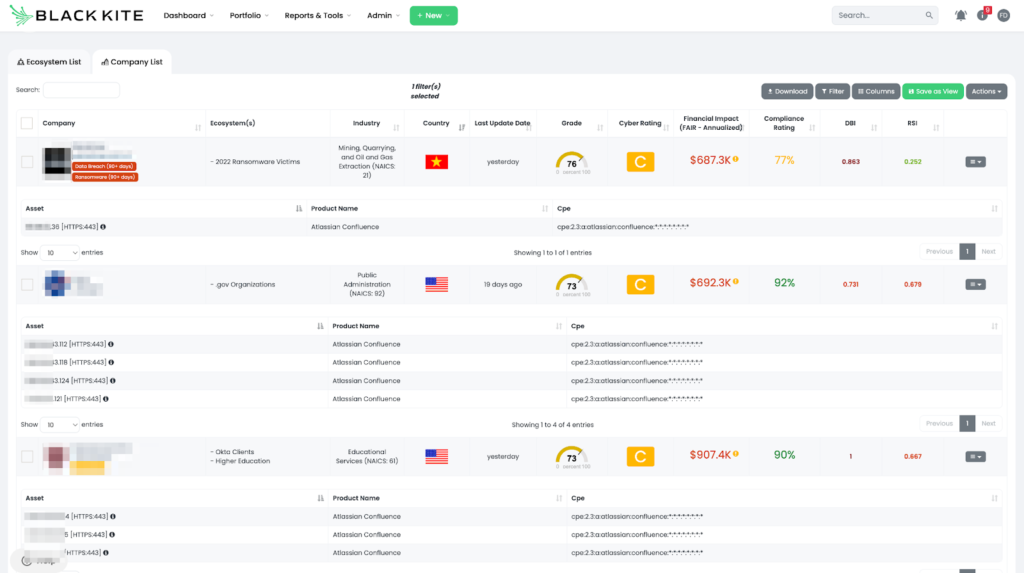
Third-party risk professionals can receive help from vendor risk intelligence tools like Black Kite to obtain such intel and act accordingly. Black Kite customers can visit their ecosystem page, where companies are listed with their cyber ratings, quantified financial risk, and ransomware susceptibility index, and filter the companies with advanced product search.
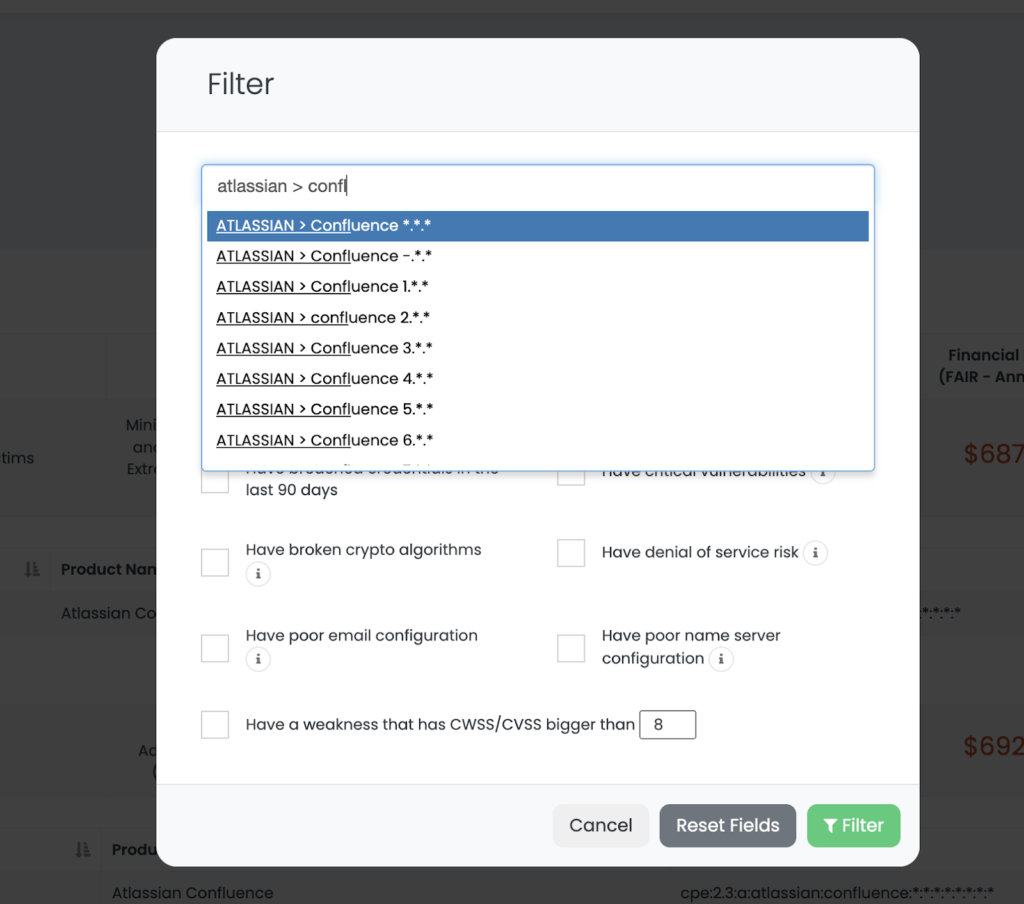
The filtered results above show the list of vendors that use Atlassian Confluence and the digital assets that have the product on them. Organizations can share this intelligence with their vendors to point them in the right direction to patch the vulnerability.
How to protect your supply chain from Atlassian Confluence RCE Vulnerability
- Identify vendors that use Atlassian Confluence
- Ask them to patch the vulnerability right away and share the mitigation steps below.
- Continuously monitor your vendors with the vulnerability
- Prioritize these vendors with other risk metrics such as a Cyber Rating or Ransomware Susceptibility Index to understand their cybersecurity posture
- Execute detailed audits with the high-risk vendors
Mitigation Steps
1. Block all internet traffic to and from Confluence Server and Data Center products until an update is available and successfully applied as US-CERT suggested.

2. Upgrade the Confluence servers: Atlassian has released versions 7.4.17, 7.13.7, 7.14.3, 7.15.2, 7.16.4, 7.17.4, and 7.18.1, which contain a fix for this issue. Organizations are advised to upgrade to the latest versions. If, for some reason, organizations are unable to patch their own servers immediately, Atlassian has provided mitigations for Confluence 7.0.0 through version 7.18.0.
3. Apply the YARA Rules here to hunt the web shell activity used during the exploitation of the vulnerability.
4. Monitor the Indicators of Compromise (IoC) such as traffic originating from suspicious IP addresses and Hash values of malicious files, listed below.
Indicators of Compromises (IoCs)
a. IP Addresses
i.
154.146.34.145
154.16.105.147
156.146.34.46
156.146.34.52
156.146.34.9
156.146.56.136
198.147.22.148
198.147.22.148
221.178.126.244
45.43.19.91
59.163.248.170
64.64.228.239
66.115.182.102
66.115.182.111
67.149.61.16
98.32.230.38
b. SHA1 Hashes
i.
4c02c3a150de6b70d6fca584c29888202cc1deef
80b327ec19c7d14cc10511060ed3a4abffc821af

