Focus Friday: TPRM Approach to SAP NetWeaver VCFRAMEWORK RCE and Apache Tomcat HTTP/2 DoS and Rewrite-Rule Bypass
Written by: Ferdi Gül
Welcome to this week’s Focus Friday, where we approach the latest critical vulnerabilities through a third-party risk management lens. We begin with SAP NetWeaver Visual Composer’s unauthenticated file upload RCE (CVE-2025-31324), a zero-day actively exploited on over 1,200 servers. Then, we turn to Apache Tomcat’s April 2025 issues—CVE-2025-31650 (HTTP/2 memory-leak DoS) and CVE-2025-31651 (rewrite-rule bypass)—which pose denial-of-service and data-exposure risks. In each section, we’ll outline key details, TPRM-specific questions, and actionable remediation steps, before demonstrating how Black Kite’s FocusTags™ streamline vendor risk identification and response.
CVE-2025-31324 in SAP NetWeaver VCFRAMEWORK
What is the SAP NetWeaver VCFRAMEWORK RCE vulnerability?
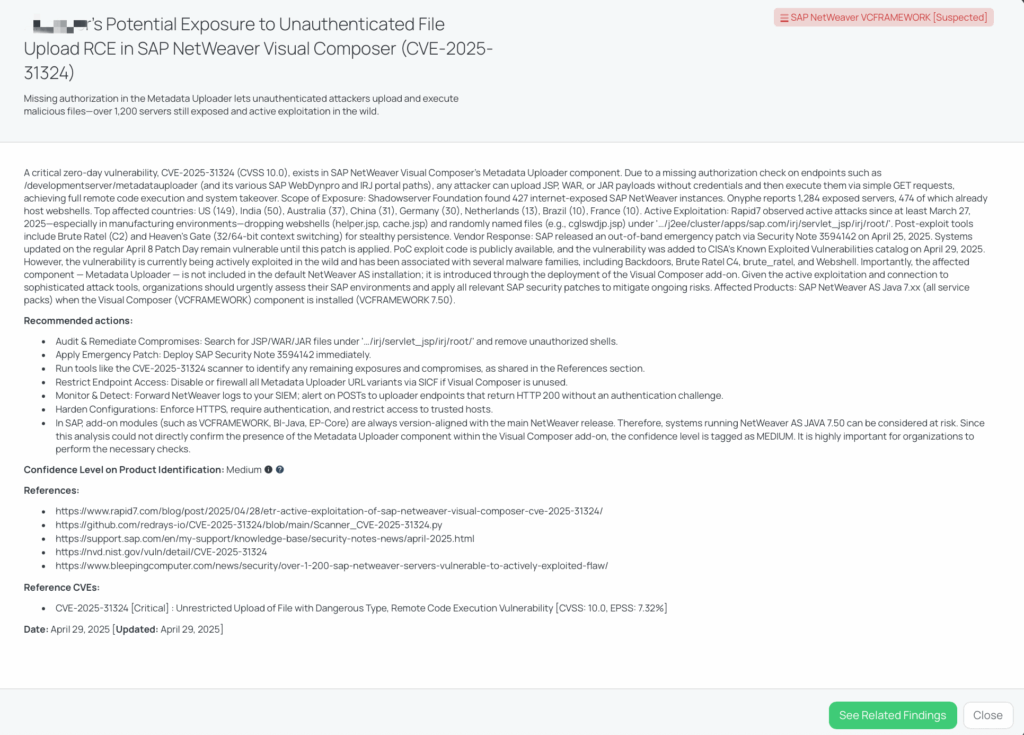
This issue is an unauthenticated file-upload flaw in the Metadata Uploader component of SAP NetWeaver Visual Composer (VCFRAMEWORK). Attackers can send crafted POST requests to /developmentserver/metadatauploaderto place JSP, WAR, or JAR payloads on the server, then invoke them via simple GET requests—achieving full remote code execution and system takeover.
It is rated Critical with a CVSS v3.1 base score of 10.0 SAP Support Portal and carries an EPSS score of 55.64%. The National Vulnerability Database first published the CVE on April 24, 2025.
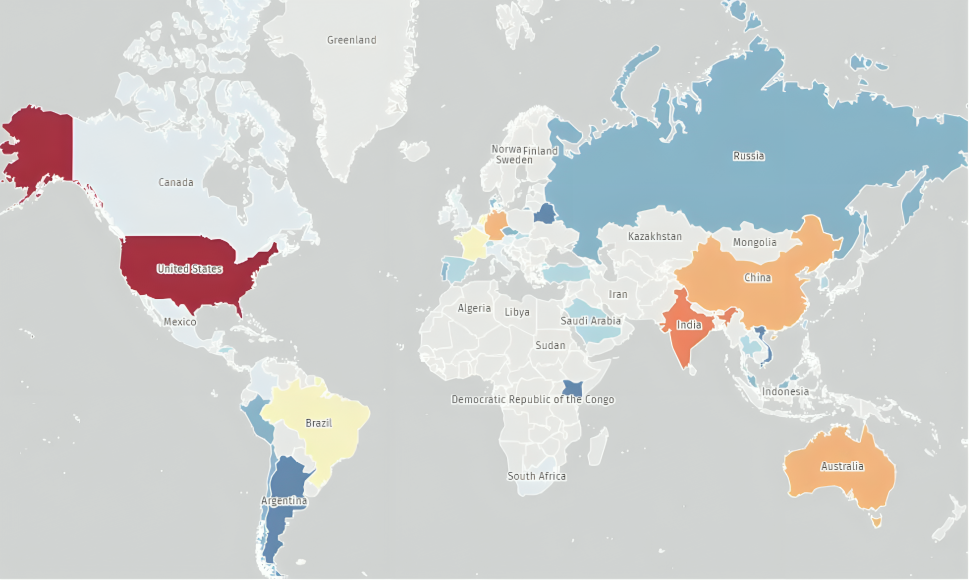
Exploitation in the wild has been observed since at least March 27, 2025, primarily targeting manufacturing environments and deploying webshells such as helper.jsp and cache.jsp. Post-exploit tooling includes Brute Ratel C2 and Heaven’s Gate for stealthy persistence (per FocusTag details).
This CVE was added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog on April 29, 2025. CISA has not issued a separate advisorial beyond the KEV entry.
Why should TPRM professionals care?
SAP NetWeaver is a widely deployed application server and development platform—often underpinning critical business processes. An unauthenticated RCE in a Visual Composer add-on can lead to full server compromise, unauthorized data access, lateral movement, and supply‐chain ripple effects. TPRM teams must ensure that any third‐party vendors using VCFRAMEWORK have assessed their exposure and applied mitigations promptly to avoid costly incident response and reputational damage.
What questions should TPRM professionals ask vendors about CVE-2025-31324?
To assess vendor risk, consider asking:
- Have you applied the emergency patch, SAP Security Note 3594142, to all instances of SAP NetWeaver AS Java 7.xx with the Visual Composer (VCFRAMEWORK) component installed to mitigate the risk of CVE-2025-31324?
- Have you conducted an audit to search for and remove unauthorized JSP/WAR/JAR files under ‘…/irj/servlet_jsp/irj/root/’ that may have been uploaded due to the vulnerability in the Metadata Uploader component of SAP NetWeaver Visual Composer?
- Have you implemented measures to restrict access to all Metadata Uploader URL variants via SICF, especially if Visual Composer is unused, to prevent unauthenticated file uploads and remote code execution?
- Are you actively monitoring your NetWeaver logs and alerting on POSTs to uploader endpoints that return HTTP 200 without an authentication challenge to detect potential exploitation of CVE-2025-31324?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors subject to this risk
Vendors should take the following steps immediately:
- Apply the Emergency Patch: Deploy SAP Security Note 3594142 (released April 25, 2025) without delay.
- Restrict Endpoint Access: Disable or firewall all Metadata Uploader URL variants via SICF if Visual Composer is unused.
- Audit & Remediate: Search for JSP/WAR/JAR files in the servlet paths and remove any unauthorized webshells.
- Monitor & Detect: Forward NetWeaver logs to your SIEM; alert on HTTP 200 POSTs to uploader endpoints that bypass authentication.
- Harden Configurations: Enforce HTTPS, require authentication on portal interfaces, and restrict access to trusted hosts.
- Run Scanners: Use available CVE-2025-31324 scanning tools to identify remaining exposures and verify remediation.
How TPRM professionals can leverage Black Kite for this vulnerability
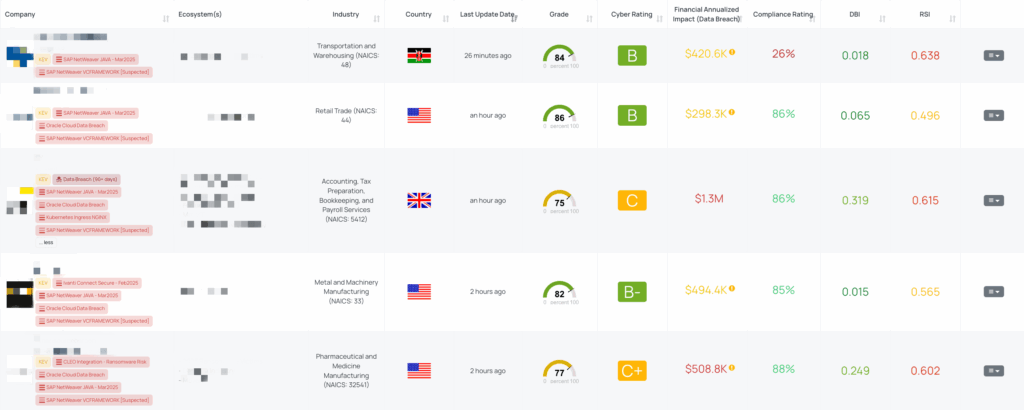
Black Kite published the SAP NetWeaver VCFRAMEWORK [Suspected] FocusTag on April 29, 2025, highlighting over 1,200 exposed servers and active exploitation trends. Within the Black Kite platform, TPRM teams can:
- Identify at-risk vendors: Automatically surface which third parties in your ecosystem host vulnerable Visual Composer instances.
- Pinpoint vulnerable assets: Obtain IP addresses and subdomains linked to exposed VCFRAMEWORK components.
- Track remediation progress: Monitor vendor patch status and anomalous telemetry around the /metadatauploader endpoint.
Drive focused outreach: Narrow questionnaires and assessments to only those vendors with confirmed exposure, reducing vendor fatigue and accelerating risk mitigation.
CVE-2025-31650 & CVE-2025-31651 in Apache Tomcat
What are the CVE-2025-31650 and CVE-2025-31651 vulnerabilities?
CVE-2025-31650 is a denial-of-service issue in Tomcat’s HTTP/2 implementation: malformed priority headers lead to incomplete request cleanup, causing a memory leak and eventual server crash. It carries a CVSS v4 score of 8.7 and an EPSS of 0.03%.
CVE-2025-31651 is a rewrite-rule bypass flaw in Tomcat’s RewriteValve: certain percent-encoded paths slip past security rules, exposing JSP shells or confidential files. It has a CVSS v3.1 score of 7.5 and an EPSS of 0.02%.
Both were first published on April 28, 2025 National Vulnerability DatabaseNational Vulnerability Database. Public proof-of-concept code exists for each, but no active exploitation has been reported and neither appears in CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog.
Why should TPRM professionals care?
Apache Tomcat powers countless web applications. A DoS can disrupt critical services and lead to business outages, while a rewrite-rule bypass can expose sensitive data and application logic. In a third-party risk context, vendors running affected versions—even if not compromised—pose material operational and data-exposure risks.
What questions should TPRM professionals ask vendors about these flaws?
To home in on true exposure, consider asking:
- Have you updated all instances of Apache Tomcat to versions 9.0.104, 10.1.40, or 11.0.6 (or later) to mitigate the risk of CVE-2025-31650 and CVE-2025-31651?
- Can you confirm if you have disabled HTTP/2 or the RewriteValve entirely if your application does not explicitly require them, as recommended in the advisory to mitigate the risk of CVE-2025-31650 and CVE-2025-31651?
- Have you implemented runtime protections such as using a reverse proxy (e.g. NGINX, Apache HTTPD) to filter out invalid HTTP/2 frames and suspicious URL-encoded paths before they reach Tomcat, as recommended in the advisory?
- Have you audited and strengthened your RewriteValve rules, including adding explicit RewriteCond checks to reject requests containing %3F, %25, or other high-risk encodings, as recommended in the advisory to mitigate the risk of CVE-2025-31651?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors subject to this risk
Vendors should:
- Upgrade to Fixed Versions: Immediately move to Apache Tomcat 9.0.104, 10.1.40, or 11.0.6 (or later).
- Harden HTTP/2 Configuration: Disable HTTP/2 if not required; otherwise, enforce valid priority header parsing at the proxy or WAF.
- Review RewriteValve Rules: Ensure canonicalization of percent-encoded paths and add explicit RewriteCond checks for high-risk encodings.
- Implement Runtime Protections: Use a reverse proxy or WAF to drop malformed HTTP/2 frames and suspicious URL-encoded requests before they reach Tomcat.
- Monitor & Alert: Instrument JVM memory metrics for early out-of-memory warnings; log and alert on anomalous priority headers or percent-encoded URIs.
How TPRM professionals can leverage Black Kite for these Apache Tomcat vulnerabilities
Black Kite published the “Apache Tomcat – Apr2025” FocusTag on April 30, 2025, highlighting both DoS (CVE-2025-31650) and rewrite-rule bypass (CVE-2025-31651) flaws. Through the platform, TPRM teams can:
- Identify exposed vendors running affected Tomcat versions with HTTP/2 or RewriteValve enabled.
- Obtain asset details—including IP addresses and subdomains—hosting vulnerable instances.
- Track patch deployment and anomalous activity around HTTP/2 and rewrite endpoints.
Target outreach to only vendors with confirmed exposure, reducing questionnaire overload and speeding mitigation.
Elevating TPRM Outcomes With Black Kite’s FocusTags™
Black Kite’s FocusTags™ are essential for transforming raw vulnerability data into TPRM-ready intelligence. With tags for SAP NetWeaver VCFRAMEWORK and Apache Tomcat’s April 2025 flaws, TPRM teams can:
- Rapid Vendor Exposure Discovery: Flag which suppliers run the vulnerable Visual Composer component or affected Tomcat versions with HTTP/2 or RewriteValve enabled.
- Precise Asset Mapping: Retrieve IP addresses and subdomain details tied to exposed servers for targeted assessments.
- Risk Prioritization: Focus remediation by combining vulnerability severity (critical RCE vs. high DoS/bypass) and vendor importance.
- Efficient Vendor Engagement: Tailor questionnaires and follow-ups only to vendors with confirmed exposures, cutting down on outreach volume.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Track patch deployment status and detect post-patch exploitation attempts around /metadatauploader endpoints or malformed HTTP/2 traffic.
By integrating these FocusTags™ into your TPRM workflow, you gain a data-driven method that accelerates vendor risk reduction and boosts overall supply-chain resilience.
Want to take a closer look at FocusTags™?
Take our platform for a test drive and request a demo today.
About Focus Friday
Every week, we delve into the realms of critical vulnerabilities and their implications from a Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) perspective. This series is dedicated to shedding light on pressing cybersecurity threats, offering in-depth analyses, and providing actionable insights.
FocusTagsTM in the Last 30 Days:
- SAP NetWeaver VCFRAMEWORK : CVE-2025-31324, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in SAP NetWeaver Visual Composer’s Metadata Uploader component.
- Apache Tomcat – Apr2025 : CVE-2025-31650, CVE-2025-31651, DoS Vulnerability, Rewrite Rule Bypass Vulnerability in Apache Tomcat.
- Fortinet Symlink Backdoor : CVE-2022-42475, CVE-2024-21762, CVE-2023-27997, Arbitrary Code Execution Vulnerability, Numeric Truncation Error, Heap-based Buffer Overflow Vulnerability, Out-of-bounds Write Vulnerability in FortiGate devices.
- SonicWall SSLVPN Gen7 : CVE-2025-32818, Null Pointer Dereference Vulnerability, DoS Vulnerability in SonicWall SSLVPN Gen 7 devices.
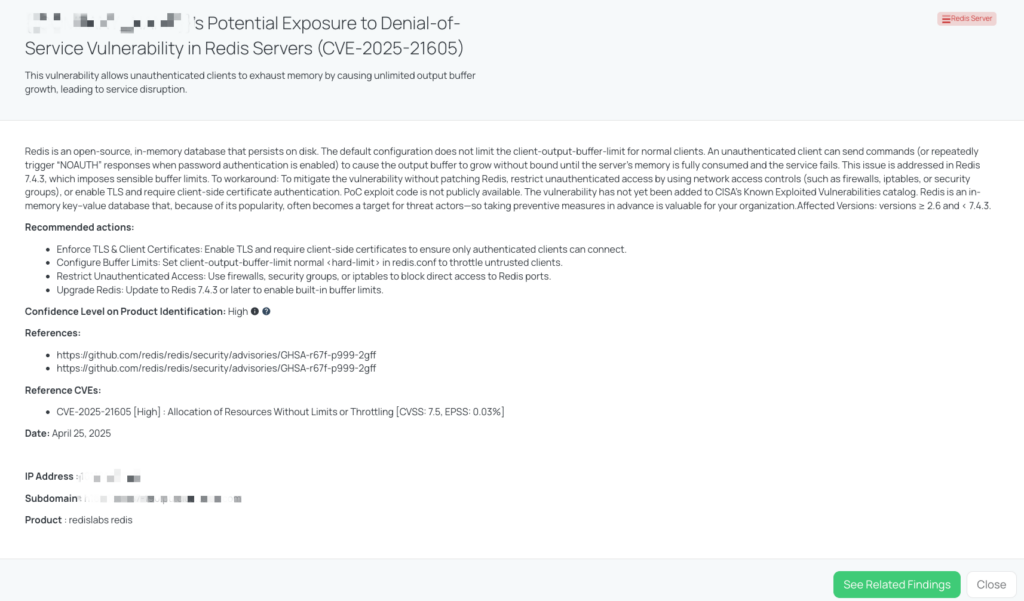
- Redis Server : CVE-2025-21605, Allocation of Resources Without Limits or Throttling in Redis Servers.
- Adobe ColdFusion : CVE-2025-24446 CVE-2025-24447 CVE-2025-30281 CVE-2025-30282 CVE-2025-30284 CVE-2025-30285 CVE-2025-30286 CVE-2025-30287 CVE-2025-30288 CVE-2025-30289 CVE-2025-30290, Deserialization of Untrusted Data, Improper Authentication, Improper Access Control, OS Command Injection, Improper Input Validation, Path Traversal Vulnerabilities in Adobe ColdFusion.
- Beego: CVE-2025-30223, Reflected/Stored XSS Vulnerabilities in Beego Web Framework.
- Ivanti Connect Secure : CVE‑2025‑22457, Stack‑based Buffer Overflow Vulnerability in Ivanti Connect Secure, Ivanti Policy Secure, and Ivanti ZTA Gateways.
- FortiSwitch : CVE‑2024‑48887, Unverified Password Change Vulnerability in Fortinet FortiSwitch web interface.
- MinIO : CVE‑2025‑31489, Improper Verification of Cryptographic Signature Vulnerability in MinIO Go module package.
- Kubernetes Ingress NGINX : CVE-2025-1097, CVE-2025-1098, CVE-2025-24514, CVE-2025-1974, Improper Isolation or Compartmentalization Vulnerability, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Kubernetes ingress-nginx controller.
- Synology DSM : CVE-2024-10441, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Synology BeeStation OS (BSM), Synology DiskStation Manager (DSM).
- Synapse Server : CVE-2025-30355, Improper Input Validation Vulnerability in Matrix Synapse Server.
- Juniper Junos OS – Mar2025 : CVE-2025-21590, Improper Isolation or Compartmentalization Vulnerability in Juniper Junos OS.
- SAP NetWeaver – Mar2025 : CVE-2017-12637, Directory Traversal Vulnerability in SAP NetWeaver Application Server.
- MongoDB – Mar2025 : CVE-2025-0755, Heap-based Buffer Overflow Vulnerability in MongoDB’s C driver library (libbson).
References
- https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-31324
- https://support.sap.com/en/my-support/knowledge-base/security-notes-news/april-2025.html
- https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/over-1-200-sap-netweaver-servers-vulnerable-to-actively-exploited-flaw/https://support.sap.com/en/my-support/knowledge-base/security-notes-news/april-2025.html
- https://www.rapid7.com/blog/post/2025/04/28/etr-active-exploitation-of-sap-netweaver-visual-composer-cve-2025-31324/
- https://dashboard.shadowserver.org/statistics/combined/time-series/?date_range=7&source=http_vulnerable&source=http_vulnerable6&tag=cve-2025-31324%2B&dataset=unique_ips&limit=1000&group_by=geo&style=stacked
- https://lists.apache.org/thread/j6zzk0y3yym9pzfzkq5vcyxzz0yzh826
- https://lists.apache.org/[email protected]
- https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-31650
- https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2025-31651
- https://securityonline.info/apache-tomcat-security-update-fixes-dos-and-rewrite-rule-bypass-flaws/
- https://github.com/absholi7ly/TomcatKiller-CVE-2025-31650/blob/main/TomcatKiller.py
- https://github.com/gregk4sec/CVE-2025-31651/blob/main/CVE-2025-31651.md

