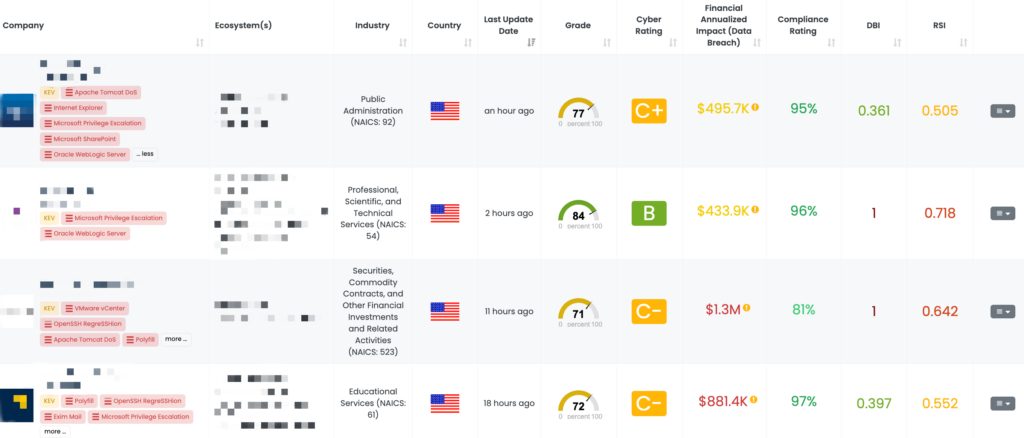
FOCUS FRIDAY: TPRM INSIGHTS INTO ORACLE WEBLOGIC SERVER AND GITHUB ENTERPRISE VULNERABILITIES
Written By: Ferdi Gül
This week’s Focus Friday blog highlights two critical vulnerabilities that pose significant risks to third-party ecosystems—CVE-2024-21216 affecting Oracle WebLogic Server and CVE-2024-9487 impacting GitHub Enterprise. These vulnerabilities, involving remote code execution and authentication bypass, respectively, threaten not only the organizations directly utilizing these products but also their entire supply chains. In this blog, we will dive into each vulnerability, its potential impact, and why Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) professionals should pay close attention. We also explore how Black Kite’s FocusTags™ can streamline your risk assessment process by identifying vendors impacted by these threats and providing actionable insights for mitigation.
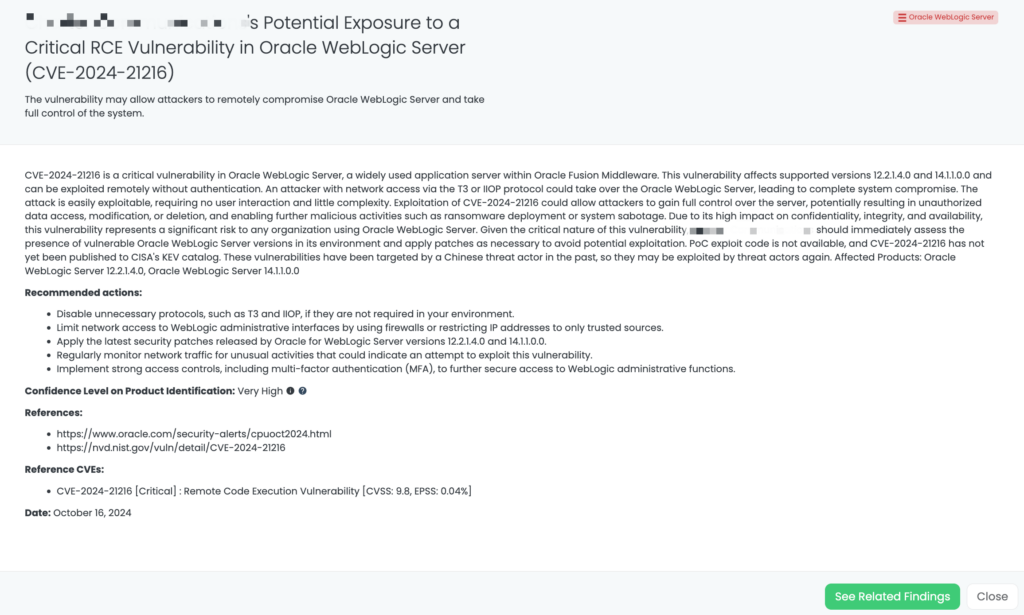
CVE-2024-21216: Oracle WebLogic Server RCE Vulnerability
What is the Oracle WebLogic Server RCE Vulnerability?
CVE-2024-21216 is a critical Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability in Oracle WebLogic Server, affecting versions 12.2.1.4.0 and 14.1.1.0.0. This vulnerability allows attackers with network access via T3 or IIOP protocol to gain full control over the server without requiring authentication. Exploitation could lead to unauthorized data access, system manipulation, and further malicious activities like ransomware deployment. The vulnerability was first published on Oracle’s October 2024 CPU and holds a CVSS score of 9.8, signifying its severity. Although no known exploitation has been reported in the wild, a PoC is not yet available. Historically, similar vulnerabilities have been exploited by Chinese threat actors.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Care About Oracle WebLogic Server RCE Vulnerability?
Oracle WebLogic Server is a widely used platform for hosting business-critical applications. A successful attack could result in complete system compromise, exposing sensitive data or enabling malicious control of the organization’s operations. This vulnerability is particularly dangerous for organizations hosting externally-facing instances of WebLogic, as it could expose them to external threats. In the context of third-party risk management, any vendors or partners using Oracle WebLogic Server should be thoroughly assessed for potential exposure, especially if these servers host sensitive applications or data.
What questions should TPRM professionals ask vendors about CVE-2024-21216?
- Have you identified any instances of Oracle WebLogic Server versions 12.2.1.4.0 or 14.1.1.0.0 in your infrastructure?
- Have you applied the security patches released by Oracle in October 2024 for the affected WebLogic Server versions?
- Are the T3 and IIOP protocols disabled if they are not necessary for your environment?
- What security controls, such as MFA and access restrictions, are in place to protect administrative access to your WebLogic servers?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors Subject to This Risk
- Immediately apply Oracle’s latest security patches for WebLogic Server versions 12.2.1.4.0 and 14.1.1.0.0.
- Disable or restrict access to T3 and IIOP protocols unless necessary for business operations.
- Implement strong access controls, including multi-factor authentication, for any WebLogic administrative interfaces.
- Limit external access to WebLogic servers by configuring firewalls or restricting IPs to trusted sources only.
- Regularly monitor network traffic for any suspicious activity targeting WebLogic servers.
How TPRM professionals can leverage Black Kite for this vulnerability
Black Kite published the Oracle WebLogic Server FocusTag on October 16, 2024, offering detailed insights into which vendors are at risk of this critical vulnerability. TPRM professionals can operationalize this FocusTag by identifying vendors using vulnerable WebLogic versions and prioritizing assessments and remediation efforts. The FocusTag also provides IP addresses and subdomains hosting the vulnerable systems, empowering organizations to act swiftly and mitigate risk efficiently. Monitoring vendors with exposure to this vulnerability through Black Kite’s intelligence platform can significantly reduce response time and mitigate potential exploitation risks.
CVE-2024-9487: GitHub Enterprise SAML SSO Authentication Bypass Vulnerability
What is the GitHub Enterprise SAML SSO Authentication Bypass Vulnerability?
CVE-2024-9487 is a critical vulnerability that affects GitHub Enterprise Server versions prior to 3.15. This vulnerability allows attackers to bypass SAML Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication, potentially granting unauthorized access to sensitive GitHub Enterprise Server instances. The issue stems from improper verification of cryptographic signatures during the SAML authentication process, which may allow attackers to bypass authentication and gain unauthorized access. This vulnerability has a CVSS score of 9.5, indicating its critical severity, and an EPSS score of 0.05%. While no known public exploitation has been reported, it poses a significant risk to enterprises that utilize GitHub Enterprise Server with SAML SSO and encrypted assertions.
The vulnerability was disclosed in October 2024 and has not yet been added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog. However, given the critical nature of the vulnerability and its potential impact on organizations, it should be addressed immediately by applying the recommended patches.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Care About the GitHub Enterprise Vulnerability?
GitHub Enterprise is widely used by organizations to manage their development environments and host proprietary code. A successful exploitation of CVE-2024-9487 could lead to unauthorized access to sensitive repositories, potentially exposing intellectual property, sensitive data, or security credentials. For TPRM professionals, the exposure of a third-party development platform like GitHub could have a cascading impact on software supply chains, making it critical to assess whether any vendors or partners are at risk due to this vulnerability.
Organizations with vendors relying on GitHub Enterprise must act swiftly to ensure that these systems are secure, as a breach could lead to unauthorized changes in code, further introducing vulnerabilities into the products and services downstream.
What questions should TPRM professionals ask vendors about CVE-2024-9487?
- Are you running any instances of GitHub Enterprise Server prior to version 3.15?
- Have you applied the necessary patches to mitigate CVE-2024-9487, especially for SAML SSO configurations?
- Is the “encrypted assertions” feature in SAML enabled on your GitHub Enterprise Server? If so, have you considered disabling it as a temporary mitigation?
- Have you implemented network access restrictions or monitoring mechanisms to detect unauthorized access attempts?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors Subject to This Risk
- Upgrade GitHub Enterprise Server to one of the following patched versions: 3.11.16, 3.12.10, 3.13.5, or 3.14.2.
- If upgrading is not feasible immediately, disable the “encrypted assertions” feature within SAML configurations to mitigate the risk temporarily.
- Restrict network access to GitHub Enterprise Server to minimize exposure and reduce the attack surface.
- Monitor user access logs and network activity for any unusual authentication events or user provisioning activities that could indicate attempted exploitation.
How TPRM professionals can leverage Black Kite for this vulnerability
Black Kite published the GitHub Enterprise FocusTag on October 14, 2024, offering in-depth insights into which vendors are exposed to this critical SAML SSO authentication bypass vulnerability. TPRM professionals can leverage this tag to identify at-risk vendors quickly, enabling faster remediation and risk mitigation. Additionally, Black Kite’s FocusTags™ provide a unique advantage by supplying the IP addresses and subdomains associated with vulnerable instances, allowing organizations to take swift, targeted action to secure their supply chain.

ENHANCING TPRM STRATEGIES WITH BLACK KITE’S FOCUSTAGS™
In an ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape, Black Kite’s FocusTags™ serve as a powerful tool to manage third-party risks efficiently. This week’s vulnerabilities in Oracle WebLogic Server and GitHub Enterprise exemplify how high-profile security flaws can cascade through supply chains, affecting multiple vendors and partners. With FocusTags™, you can stay ahead of these threats by:
- Instant Risk Identification: Quickly pinpoint which vendors in your supply chain are impacted by emerging vulnerabilities like CVE-2024-21216 and CVE-2024-9487, ensuring a fast and focused response.
- Risk Prioritization: FocusTags™ allow you to prioritize risks based on the criticality of affected vendors and the severity of vulnerabilities, ensuring your TPRM efforts are aligned with the highest potential risks.
- Vendor Engagement: Black Kite’s FocusTags™ equip you with detailed insights that facilitate meaningful discussions with your vendors, particularly about how they are addressing these specific vulnerabilities.
- Holistic Cybersecurity Posture: By providing a comprehensive view of the threat landscape, FocusTags™ enhance your overall cybersecurity strategy, helping you to address not just the vulnerabilities of today but also prepare for the risks of tomorrow.
Black Kite’s FocusTags™ continue to be an invaluable asset for TPRM professionals, offering real-time insights and targeted recommendations to help mitigate third-party risks associated with high-profile vulnerabilities.
Want to take a closer look at FocusTags™?
Take our platform for a test drive and request a demo today.
About Focus Friday
Every week, we delve into the realms of critical vulnerabilities and their implications from a Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) perspective. This series is dedicated to shedding light on pressing cybersecurity threats, offering in-depth analyses, and providing actionable insights.
FocusTags™ in the Last 30 Days:
- Oracle WebLogic Server: CVE-2024-21216, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Oracle WebLogic Server.
- GitHub Enterprise: CVE-2024-9487, SAML SSO Authentication Bypass Vulnerability in GitHub Enterprise Server.
- Fortinet Core Products: CVE-2024-23113, Format String Vulnerability in FortiOS, FortiPAM, FortiProxy, and FortiWeb.
- Cisco RV Routers: CVE-2024-20393, CVE-2024-20470, Privilege Escalation and RCE Vulnerability in RV340, RV340W, RV345, and RV345P Dual WAN Gigabit VPN Routers.
- Ivanti Connect Secure: CVE-2024-37404, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Ivanti Connect Secure & Policy Secure.
- Zimbra: CVE-2024-45519, Remote Command Execution Vulnerability in Zimbra.
- DrayTek Routers: CVE-2020-15415, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in DrayTek Vigor Routers.
- Authentik: CVE-2024-47070, Authentication Bypass Vulnerability in Authentik.
- Octopus Deploy: CVE-2024-9194, SQL Injection Vulnerability in Octopus Server.
- pgAdmin: CVE-2024-9014, OAuth2 Authentication Vulnerability in pgAdmin.
- Keycloak: CVE-2024-8698, CVE-2024-8883, SAML Signature Validation Bypass and Session Hijacking Vulnerability in Keycloak.
- Navidrome: CVE-2024-47062, SQL Injection Vulnerability in Navidrome.
- PAN-OS Cleartext: CVE-2024-8687, Cleartext Exposure Security Flaw in PAN-OS, GlobalProtect, Prisma Access.
- FileCatalyst Workflow: CVE-2024-6633, CVE-2024-6632, Insecure Default Configuration and SQL Injection Vulnerability in Fortra FileCatalyst Workflow.
- WPML: CVE-2024-6386, Critical Remote Code Execution Vulnerability via Twig Server-Side Template Injection in WPML Plugin
- SonicWall Firewalls: CVE-2024-40766, Critical Improper Access Control Vulnerability in SonicWall Firewalls
- Dahua IP Camera: CVE-2021-33045, CVE-2021-33044, Critical Authentication Bypass Vulnerabilities in Dahua IP Camera Systems
References
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-21216
https://www.oracle.com/security-alerts/cpuoct2024.html
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-9487
https://docs.github.com/en/[email protected]/admin/release-notes#3.14.2

