FOCUS FRIDAY: THIRD-PARTY RISK INSIGHTS ON ZIMBRA, DrayTek ROUTERS, AUTHENTIK, AND OCTOPUS DEPLOY VULNERABILITIES
Written By: Ferdi Gül
Contributor: Ferhat Dikbiyik
Welcome to this week’s edition of Focus Friday, where we dive into critical vulnerabilities affecting the third-party ecosystem from a Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) perspective. As organizations face mounting pressure to manage vulnerabilities swiftly and effectively, identifying and addressing these threats becomes crucial for maintaining cybersecurity resilience. In today’s blog, we will explore significant vulnerabilities affecting widely used platforms like Zimbra, DrayTek Routers, Authentik, and Octopus Deploy. These vulnerabilities pose significant risks, potentially allowing unauthorized access, remote command execution, and data breaches. We’ll provide actionable insights and discuss how TPRM professionals can leverage Black Kite’s FocusTags™ to mitigate these risks effectively.
CVE-2024-45519: Zimbra Remote Command Execution Vulnerability
What Is the Zimbra Remote Command Execution Vulnerability?
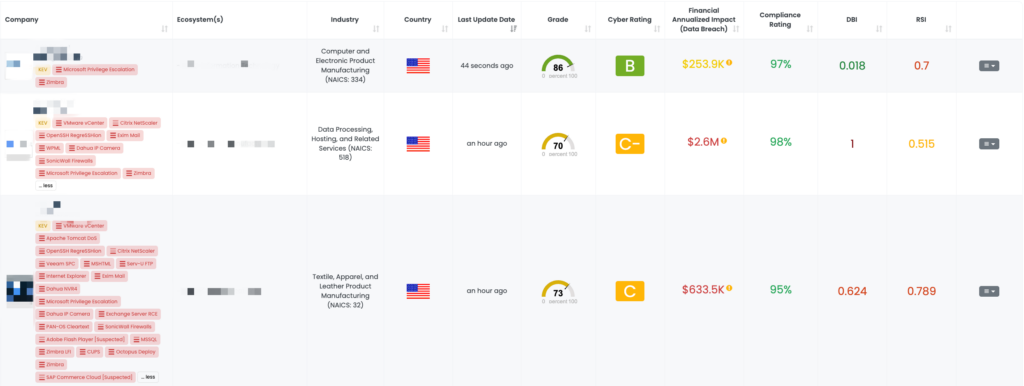
CVE-2024-45519 is a critical vulnerability in the Zimbra Collaboration Suite that allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary commands remotely on unpatched Zimbra servers. This vulnerability is caused by improper sanitization of user input within the postjournal service, where the ‘popen’ function is used to construct and execute commands from SMTP recipient addresses. Attackers can exploit this flaw by sending specially crafted SMTP messages that inject malicious commands, leading to unauthorized remote command execution.
The vulnerability, discovered in September 2024, has a high CVSS score of 9.0, marking it as a severe threat. Although no active exploitation has been reported, researchers demonstrated PoC exploits capable of compromising the entire system. This vulnerability has not yet been added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog, but it poses a significant risk if left unpatched. The vulnerability in Zimbra Collaboration could potentially be exploited by attackers with the right tools and knowledge, as Zimbra has been a frequent target for malicious actors.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Care About the Zimbra Vulnerability?
TPRM professionals should pay close attention to this vulnerability due to the critical role that Zimbra plays in email communication and collaboration for many organizations. An attack on this platform can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive emails and files, installation of malware, and further attacks on internal systems. The remote nature of the attack and the unauthenticated access make it particularly dangerous, as threat actors can exploit vulnerable Zimbra instances without any prior credentials.
In addition, Zimbra has historically been a target for malicious actors, increasing the likelihood that threat actors will attempt to leverage CVE-2024-45519 in future campaigns. The potential for full system compromise makes this a high-priority vulnerability for vendor risk management.
What Questions Should TPRM Professionals Ask Vendors About the Zimbra Vulnerability?
To address the risk posed by CVE-2024-45519, TPRM professionals should ask the following questions:
- Have you applied the latest security patches to Zimbra Collaboration Suite, specifically versions 9.0.0 Patch 41, 10.0.9, 10.1.1, or 8.8.15 Patch 46?
- Have you disabled the postjournal service if it is not required in your Zimbra environment? If so, what procedures have been followed to ensure this service is not in use?
- Are input sanitization rules and filtering mechanisms in place to prevent the execution of dangerous SMTP commands?
- What monitoring and detection measures are implemented to identify potential exploitation attempts via SMTP?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors Subject to This Risk
Vendors with Zimbra installations should follow these remediation steps to mitigate the risk of CVE-2024-45519:
- Patch immediately: Update to the latest versions of Zimbra Collaboration Suite, which include critical fixes.
- Disable unnecessary services: If the ‘postjournal’ service is not required, disable it using the appropriate Zimbra configuration commands.
- Enforce input validation: Apply strong input sanitization to SMTP commands to prevent malicious injections.
- Monitor SMTP traffic: Set up continuous monitoring for unusual or malicious SMTP activity that could indicate exploitation attempts.
- Network segmentation: Implement network segmentation to limit lateral movement if a Zimbra system is compromised.
How Can TPRM Professionals Leverage Black Kite for This Vulnerability?
Black Kite helps TPRM professionals quickly identify vendors potentially affected by CVE-2024-45519. The FocusTag for Zimbra was published on September 30, 2024, providing users with critical intelligence about vulnerable Zimbra assets within their vendor ecosystem. This intelligence includes IP addresses and subdomains that are associated with vulnerable Zimbra servers.
CVE-2020-15415: DrayTek Routers Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
What Is the DrayTek Routers Remote Code Execution Vulnerability?
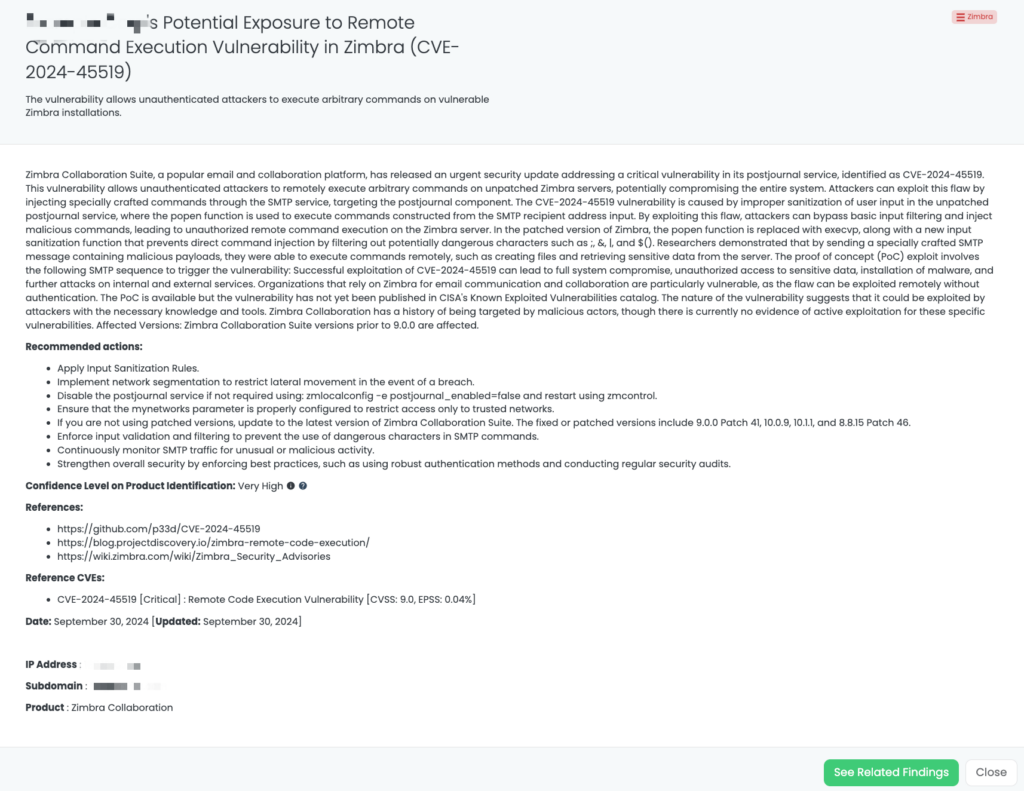
CVE-2020-15415 is a critical remote code execution vulnerability impacting DrayTek Vigor3900, Vigor2960, and Vigor300B routers. This vulnerability arises from improper validation of filenames with shell metacharacters during the upload of configuration files via the WebUI endpoint cgi-bin/mainfunction.cgi/cvmcfgupload. By exploiting this flaw, attackers can send specially crafted HTTP POST requests that allow them to execute arbitrary commands on the affected devices, potentially compromising the entire system.
With a CVSS score of 9.8, this vulnerability is categorized as critical. The EPSS score is 94.31%, indicating a notable chance of exploitation. The vulnerability was added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog on September 30, 2024, highlighting its severity and risk of exploitation in the wild. Proof-of-concept exploits are available, increasing the likelihood of malicious actors targeting vulnerable systems.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Care About the DrayTek Routers Vulnerability?
DrayTek routers play a significant role in network infrastructure for businesses, providing remote access and connectivity across multiple devices. A remote code execution vulnerability on these devices could lead to unauthorized access, data exfiltration, and complete system compromise. Given that these routers may be deployed in critical business environments, the impact of a breach could extend beyond the initial router, leading to further network infiltration or exploitation of connected systems.
For TPRM professionals, ensuring that vendors using DrayTek routers are secured against CVE-2020-15415 is vital to preventing unauthorized access to critical data or systems. Exploitation could enable attackers to carry out further attacks, such as malware installation or network manipulation.
What Questions Should TPRM Professionals Ask Vendors About the DrayTek Routers Vulnerability?
To mitigate the risk associated with CVE-2020-15415, TPRM professionals should consider asking vendors the following questions:
- Have you applied the firmware update released by DrayTek for Vigor3900, Vigor2960, and Vigor300B routers to address CVE-2020-15415?
- Are you limiting remote administrative access to trusted IP addresses using an Access Control List (ACL)?
- Have you disabled remote administration on affected devices if it is not necessary?
- What monitoring procedures are in place to detect any unusual or malicious activity on your DrayTek routers?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors Subject to This Risk
Vendors using DrayTek routers should follow these remediation steps:
- Firmware Update: Upgrade to the latest firmware (1.5.1.1 or later) to patch the vulnerability.
- Disable Remote Access: If immediate upgrading is not feasible, disable remote access to the affected routers or restrict access using ACLs.
- Use Secure Remote Administration: Switch to secure methods such as VPN or VigorACS for remote device administration.
- Monitor Device Activity: Regularly monitor traffic and system logs for unusual activity that may indicate an attempted or successful exploit.
- Regular Firmware Checks: Ensure that firmware is kept up to date across all DrayTek devices to mitigate exposure to future vulnerabilities.
How Can TPRM Professionals Leverage Black Kite for This Vulnerability?
Black Kite provides valuable insights by identifying vendors using potentially vulnerable DrayTek routers affected by CVE-2020-15415. The FocusTag for DrayTek routers was published on September 30, 2024, offering actionable intelligence on vulnerable assets, including device IP addresses and configurations. By leveraging this data, TPRM professionals can quickly narrow down at-risk vendors and prioritize outreach to those most vulnerable to attack.
CVE-2024-47070: Authentik Authentication Bypass Vulnerability
What Is the Authentik Authentication Bypass Vulnerability?
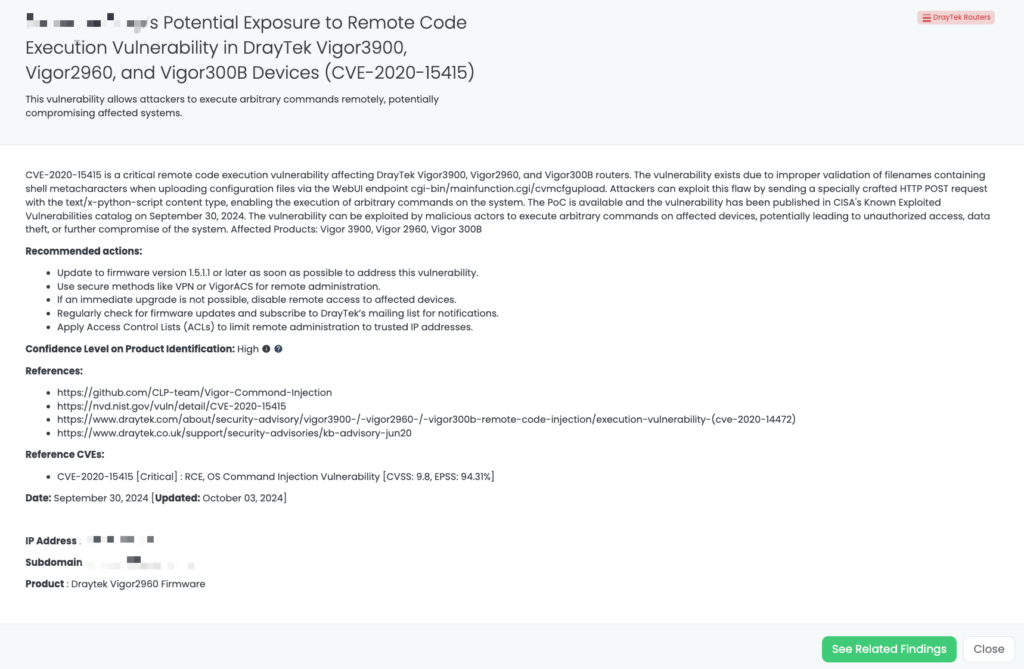
CVE-2024-47070 is a critical vulnerability in Authentik, an open-source Identity Provider (IdP) and Single Sign-On (SSO) platform. The flaw exists due to improper handling of the X-Forwarded-For HTTP header in reverse proxy setups. Attackers can manipulate this header by sending an unparsable value (e.g., “a”), which tricks Authentik into bypassing password authentication policies. This allows unauthorized access to user accounts if the attacker knows the login or email address, bypassing the need for the correct password.
This vulnerability has a CVSS score of 9.0, marking it as critical. It affects Authentik versions up to and including 2024.8.2 and 2024.6.4. While no active exploitation or PoC has been publicly released, the risk remains significant, especially in environments where Authentik is accessible without a properly configured reverse proxy.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Care About the Authentik Vulnerability?
TPRM professionals should be highly concerned about CVE-2024-6386 due to its potential impact on WordPress sites using the WPML plugin. WordPress is a widely adopted content management system, and any vulnerability that allows for remote code execution poses a substantial risk. An attacker exploiting this vulnerability could gain unauthorized control over a website, execute malicious code, manipulate content, steal sensitive data, or even deface the site. In environments where WordPress sites are used for critical business functions, such a compromise could lead to significant data breaches, reputational damage, and operational disruptions. It is crucial for TPRM professionals to ensure that their vendors using WordPress and the WPML plugin are aware of this vulnerability and have implemented appropriate measures to mitigate the risk.
What Questions Should TPRM Professionals Ask Vendors About the Authentik Vulnerability?
To address the risk posed by CVE-2024-47070, TPRM professionals should ask vendors the following questions:
- Have you upgraded to Authentik version 2024.6.5 or 2024.8.3 to address CVE-2024-47070?
- Is your reverse proxy correctly configured to set valid X-Forwarded-For headers, ensuring that this vulnerability cannot be exploited?
- What measures are in place to monitor and detect suspicious activity related to authentication bypass attempts in your system?
- Have you disabled direct internet exposure of Authentik where possible, or applied proper access controls if external access is required?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors Subject to This Risk
Vendors using Authentik should follow these remediation steps:
- Apply Patches: Upgrade to Authentik versions 2024.6.5 or 2024.8.3, which include the fixes for CVE-2024-47070.
- Configure Reverse Proxy: Ensure that the reverse proxy is set to properly handle and validate the X-Forwarded-For header.
- Limit Direct Exposure: Avoid exposing Authentik directly to the internet without a secure reverse proxy configuration.
- Manual Workaround: If patching is not immediately possible, set the “Failure result” option on policy bindings to “Pass” to prevent authentication policy bypass, though this is a temporary and less secure workaround.
- Monitor Traffic: Continuously monitor network and authentication logs for unusual activities that may indicate exploitation attempts.
How Can TPRM Professionals Leverage Black Kite for This Vulnerability?
Black Kite enables TPRM professionals to swiftly identify vendors using vulnerable versions of Authentik through its FocusTag system. The FocusTag for Authentik was published on October 1, 2024, providing comprehensive intelligence on at-risk vendors, including specific vulnerable assets. With this information, TPRM teams can prioritize remediation efforts, focusing on vendors using outdated or misconfigured Authentik systems.
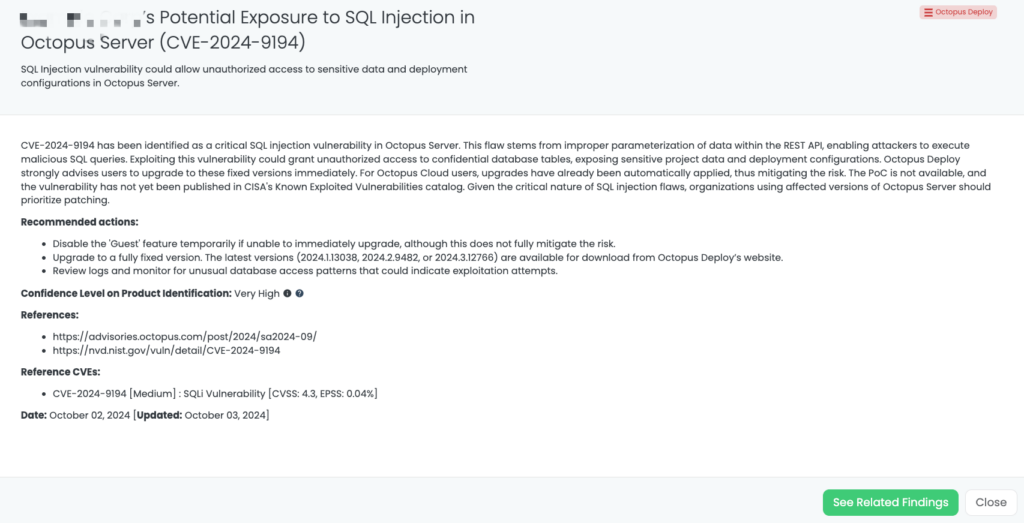
CVE-2024-9194: Octopus Deploy SQL Injection Vulnerability
What Is the Octopus Deploy SQL Injection Vulnerability?
CVE-2024-9194 is a high-severity SQL injection vulnerability in Octopus Server. This vulnerability is due to improper parameter handling within the REST API, which allows attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands. By exploiting this flaw, attackers could gain unauthorized access to the database, potentially exposing sensitive project data and deployment configurations.
This vulnerability has a CVSS score of 8.7. Although there is no active exploitation or available PoC, the critical nature of SQL injection vulnerabilities makes this a significant concern. The vulnerability was discovered in October 2024, and organizations using affected versions of Octopus Server are strongly advised to prioritize patching.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Care About the Octopus Deploy Vulnerability?
SQL injection vulnerabilities can have a significant impact on an organization, as they may allow attackers to access or manipulate sensitive data. Octopus Server is commonly used to manage application deployments, and unauthorized access to its configurations could lead to major disruptions in the deployment process. Additionally, sensitive data related to projects and infrastructure could be exposed.
For TPRM professionals, this vulnerability poses a risk to any vendors relying on Octopus Deploy for their DevOps and deployment workflows. Unauthorized access to these systems could result in data leakage, malicious code injection, or compromised deployments, which could directly impact business operations.
What Questions Should TPRM Professionals Ask Vendors About the Octopus Deploy Vulnerability?
To mitigate the risks associated with CVE-2024-9194, TPRM professionals should ask vendors the following questions:
- Have you upgraded to the fixed versions of Octopus Server (2024.1.13038, 2024.2.9482, or 2024.3.12766) to address CVE-2024-9194?
- If patching is not immediately possible, have you disabled the “Guest” feature to reduce the risk of exploitation?
- What measures are in place to monitor and log database access for unusual or suspicious activity?
- How are you ensuring the security of deployment configurations to prevent unauthorized access or modification?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors Subject to This Risk
Vendors using Octopus Deploy should follow these remediation steps:
- Apply Patches: Upgrade to the fixed versions (2024.1.13038, 2024.2.9482, or 2024.3.12766) as soon as possible to mitigate the vulnerability.
- Disable Guest Access: Temporarily disable the “Guest” feature if patching is not immediately feasible.
- Monitor Database Access: Implement continuous monitoring of database logs and activities to detect any unusual access patterns.
- Review Deployment Security: Regularly review and update deployment configurations to ensure they are secure and inaccessible to unauthorized users.
How Can TPRM Professionals Leverage Black Kite for This Vulnerability?
Black Kite provides detailed intelligence on vendors affected by CVE-2024-9194, helping TPRM professionals identify and prioritize remediation efforts. The FocusTag for Octopus Deploy was published on October 2, 2024, offering insights into vulnerable assets, including details about affected versions and system configurations. This allows organizations to quickly assess their third-party risks and focus on ensuring that vendors using Octopus Deploy have patched their systems.
Black Kite’s asset-based approach enables TPRM teams to operationalize this data, reducing the time and effort needed to address the vulnerability. By providing specific asset information, Black Kite makes it easier for professionals to take immediate action to mitigate the risks posed by this SQL injection vulnerability.
Maximizing TPRM Effectiveness With Black Kite’s FocusTags™
In the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape, Black Kite’s FocusTags™ are instrumental in enhancing Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) strategies. By offering real-time insights into emerging vulnerabilities, these tags enable TPRM professionals to stay ahead of potential risks and make informed decisions regarding vendor security.
Here’s how Black Kite’s FocusTags™ empower organizations to effectively manage vulnerabilities like those in Zimbra, DrayTek Routers, Authentik, and Octopus Deploy:
- Dynamic Risk Identification: Instantly highlight vendors impacted by critical vulnerabilities, allowing for rapid response and mitigation efforts.
- Risk-Based Prioritization: Enable the prioritization of vulnerabilities based on the severity of the risk and the importance of the affected vendors, ensuring resources are allocated efficiently.
- Enhanced Vendor Engagement: Provide TPRM teams with the necessary tools to engage vendors in meaningful discussions about their security posture and remediation strategies.
- Strengthening Cybersecurity Posture: Deliver a comprehensive view of the current threat landscape, supporting the development of stronger and more adaptive cybersecurity strategies.
By transforming complex vulnerability data into actionable intelligence, Black Kite’s FocusTags™ make it easier for organizations to tackle critical vulnerabilities and safeguard their third-party ecosystems. With real-time updates and deep insights into vendor exposures, Black Kite helps TPRM professionals mitigate risks proactively and effectively.
Want to take a closer look at FocusTags™?
Take our platform for a test drive and request a demo today.
About Focus Friday
Every week, we delve into the realms of critical vulnerabilities and their implications from a Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) perspective. This series is dedicated to shedding light on pressing cybersecurity threats, offering in-depth analyses, and providing actionable insights.
FocusTags™ in the Last 30 Days:
- Zimbra: CVE-2024-45519, Remote Command Execution Vulnerability in Zimbra.
- DrayTek Routers: CVE-2020-15415, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in DrayTek Vigor Routers.
- Authentik: CVE-2024-47070, Authentication Bypass Vulnerability in Authentik.
- Octopus Deploy: CVE-2024-9194, SQL Injection Vulnerability in Octopus Server.
- pgAdmin: CVE-2024-9014, OAuth2 Authentication Vulnerability in pgAdmin.
- Keycloak: CVE-2024-8698, CVE-2024-8883, SAML Signature Validation Bypass and Session Hijacking Vulnerability in Keycloak.
- Navidrome: CVE-2024-47062, SQL Injection Vulnerability in Navidrome.
- PAN-OS Cleartext: CVE-2024-8687, Cleartext Exposure Security Flaw in PAN-OS, GlobalProtect, Prisma Access.
- FileCatalyst Workflow: CVE-2024-6633, CVE-2024-6632, Insecure Default Configuration and SQL Injection Vulnerability in Fortra FileCatalyst Workflow.
- WPML: CVE-2024-6386, Critical Remote Code Execution Vulnerability via Twig Server-Side Template Injection in WPML Plugin
- SonicWall Firewalls: CVE-2024-40766, Critical Improper Access Control Vulnerability in SonicWall Firewalls
- Dahua IP Camera: CVE-2021-33045, CVE-2021-33044, Critical Authentication Bypass Vulnerabilities in Dahua IP Camera Systems
- Microsoft Privilege Escalation Vulnerability: CVE-2024-38193, CVE-2024-38106, CVE-2024-38107, Critical Privilege Escalation Vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows
- SolarWinds WHD: CVE-2024-28986, Critical Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in SolarWinds Web Help Desk
- Zimbra LFI: CVE-2024-33535, Local File Inclusion Vulnerability in Zimbra Collaboration Suite
- Exchange Server RCE: CVE-2021-31196, CVE-2021-34473, Remote Code Execution Vulnerabilities in Microsoft Exchange Server
References
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-45519
https://wiki.zimbra.com/wiki/Zimbra_Security_Advisories
https://blog.projectdiscovery.io/zimbra-remote-code-execution
https://github.com/p33d/CVE-2024-45519
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2020-15415
https://www.draytek.co.uk/support/security-advisories/kb-advisory-jun20
https://github.com/CLP-team/Vigor-Commond-Injection
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-47070
https://github.com/goauthentik/authentik/security/advisories/GHSA-7jxf-mmg9-9hg7

