Vendor Evaluation
Get the full cyber posture, breach history, and compliance standing of your vendors before they touch your data.
EVALUATE RISK about
Every Supplier. Every Risk.
Your single source of truth for vendor cyber risk, enabling you to act faster, reduce exposure, and stay ahead of threats.
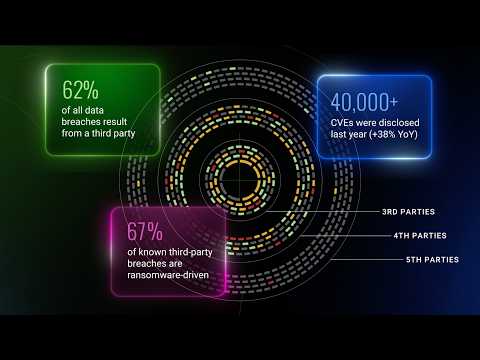
Your business doesn’t run in isolation. It runs on a complex web of vendors, partners, and suppliers. When one of them gets hit, you feel it.
Black Kite surfaces the cyber risks buried deep in your vendor ecosystem before they escalate. With evidence-based insight, you can move faster, prioritize what matters, and stop risk before it spreads.

Vendor questionnaires and point-in-time scores only show you the tip of the iceberg. Real resilience comes from seeing what lies beneath. Black Kite reveals the deeper signals: ransomware susceptibility, regulatory gaps, financial exposure, and more, so you can act early and explain why.
Black Kite is the cyber third-party risk intelligence platform built for enterprise scale. From cyber assessments to continuous monitoring and risk response, we give TPRM teams the tools to manage risk across their entire ecosystem without guesswork.
Every product is mapped to business outcomes, so you can move faster, show your work, and stay ahead of whatever comes next.


We know you're up against a lot. That's why we've built a platform that tackles your most critical third-party risk challenges head-on. No more guessing. No more scrambling. Just clear vision and decisive action.
Get the full cyber posture, breach history, and compliance standing of your vendors before they touch your data.
EVALUATE RISK aboutGain real-time visibility, detect high-risk events, and track nth-party relationships. Know what's happening, instantly.
MONITOR RISK aboutTurn risk intelligence into clear, collaborative action. Share specifics, assign tasks, and track remediation, all in one place.
RESPOND TO RISK aboutAutomate assessments, integrate with your GRC, and keep all your documentation audit-ready.
STAY COMPLIANT about
A financial lens on cyber risk. Calculates the probable economic impact of a breach using the industry-standard Open FAIR™ model, helping you prioritize what matters most.