FOCUS FRIDAY: TPRM INSIGHTS ON SERV-U FTP, MICROSOFT SHAREPOINT, CITRIX NETSCALER, SERVICENOW, EXIM MAIL, AND GEOSERVER INCIDENTS WITH BLACK KITE’S FOCUSTAGS™
Written By: Ferdi Gul
Contributor: Ferhat Dikbiyik
Welcome to this week’s Focus Friday blog, where we delve into some of the most pressing vulnerabilities affecting various critical systems from a Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) perspective. This week, we spotlight vulnerabilities in Serv-U FTP, Microsoft SharePoint, Citrix NetScaler, ServiceNow, Exim Mail, and GeoServer. Each of these vulnerabilities presents unique challenges and risks, and we explore how Black Kite’s FocusTags™ provide actionable insights to effectively manage and mitigate these threats. Join us as we break down these vulnerabilities and offer guidance on leveraging FocusTags™ for enhanced TPRM strategies.
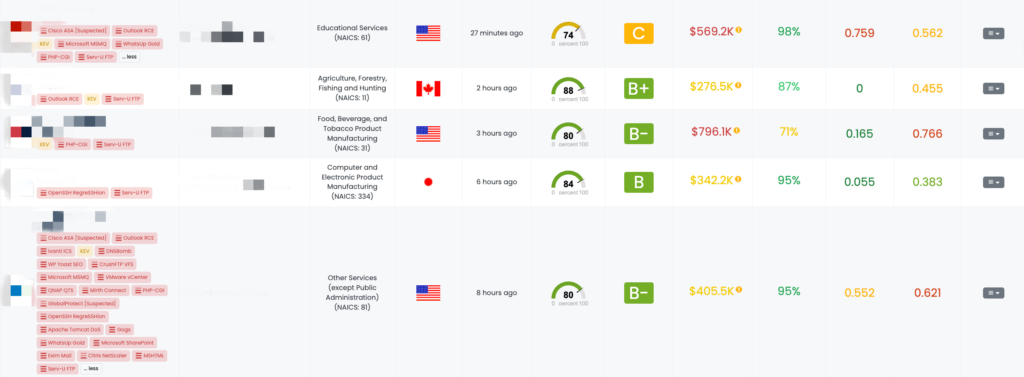
CVE-2024-28995: Directory Traversal Vulnerability in SolarWinds Serv-U
What is the Directory Traversal Vulnerability in SolarWinds Serv-U?
CVE-2024-28995 is a directory traversal vulnerability in SolarWinds Serv-U. This vulnerability arises due to improper handling of user-supplied input in file paths. An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by sending a specially crafted request containing directory traversal sequences (e.g., ../). This can allow the attacker to read or write files outside the intended directories, potentially leading to unauthorized access to sensitive files and system compromise. The vulnerability is classified as a directory traversal with a severity level of High. It has a CVSS score of 7.5 and an EPSS score of 77.48%.
Publicly disclosed on June 13, 2024, this vulnerability has been actively exploited in the wild by threat actors. The attack campaign is likely conducted by a Chinese-speaking attacker, who refines their exploits with each attempt. The vulnerability was added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog on July 17, 2024, with a CISA advisory published on the same date.
Why should TPRM professionals care about the Directory Traversal Vulnerability in SolarWinds Serv-U?
TPRM professionals should be concerned about this vulnerability because it poses a significant risk to any organization using SolarWinds Serv-U. Exploiting this vulnerability can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive information, including system passwords and configuration files. This type of access can compromise the entire system, allowing attackers to execute further malicious activities such as data theft, system manipulation, and spreading malware.
Given the severity and active exploitation of CVE-2024-28995, TPRM professionals need to prioritize assessing and mitigating this risk among their vendors. Ensuring that vendors are aware of and addressing this vulnerability is crucial to maintaining the security and integrity of the supply chain.
What questions should TPRM professionals ask vendors about the Directory Traversal Vulnerability in SolarWinds Serv-U?
- Have you updated your SolarWinds Serv-U systems to version 15.4.2 HF2 or later to mitigate CVE-2024-28995? Can you confirm the successful installation of this update?
- Can you outline the specific steps taken to secure your SolarWinds Serv-U systems against CVE-2024-28995, including any changes to file access configurations?
- What monitoring tools do you have in place to detect potential exploitation of CVE-2024-28995?
- How do you validate and sanitize user inputs in your SolarWinds Serv-U configurations to prevent directory traversal attacks?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors subject to this risk
To address the risks associated with CVE-2024-28995, vendors should take the following actions:
- Ensure that systems are updated to SolarWinds Serv-U version 15.4.2 HF2 or later.
- These measures help prevent unauthorized access even if some information is disclosed.
- Allow access only from trusted IP addresses to reduce the risk of exploitation.
- Monitor network traffic for unusual activities. Use intrusion detection and prevention systems to identify and respond to potential attacks.
- Validate and sanitize user inputs.Ensure that any user-supplied input is properly validated and sanitized to prevent directory traversal attacks.
How TPRM professionals can leverage Black Kite for this vulnerability
Black Kite helps TPRM professionals determine which vendors are affected by CVE-2024-28995. The FocusTag provides critical asset information, such as IP addresses and subdomains, that pose risks associated with this vulnerability. This targeted intelligence allows TPRM professionals to prioritize their efforts and effectively manage the risk within their supply chain.
Black Kite published the FocusTag for CVE-2024-28995 on July 17, 2024. By leveraging this FocusTag, TPRM professionals can quickly identify at-risk vendors and take appropriate actions to mitigate the impact of this vulnerability.

CVE-2024-38094: Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint
What is the Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint?
CVE-2024-38094 is a critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting Microsoft SharePoint Servers. This vulnerability allows an attacker to exploit SharePoint by sending a specially crafted HTTP request, which manipulates SharePoint’s parsing of web requests. This manipulation leads to arbitrary code execution with system-level privileges. Given the widespread use of SharePoint for enterprise collaboration and document management, the exploitation of this vulnerability can have severe consequences, including data theft, unauthorized access to sensitive information, and disruption of business operations.
This RCE vulnerability is classified as High severity, with a CVSS score of 7.2 and an EPSS score of 0.05%. The PoC exploit code was published on July 10, 2024, making the vulnerability particularly dangerous due to the availability of exploit code. Although it is not yet listed in CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, its critical nature and potential impact make it a significant threat. A threat actor with Site Owner permissions could exploit these flaws to execute arbitrary code on SharePoint Server, risking data breaches, service disruptions, or complete system compromise. The vulnerability is also related to CVE-2024-38023, and CVE-2024-38024.
Why should TPRM professionals care about the RCE Vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint?
TPRM professionals should be highly concerned about this vulnerability because it affects a core enterprise platform used for collaboration and document management. The exploitation of this vulnerability can lead to severe outcomes such as data breaches, unauthorized access to sensitive information, and significant disruption of business operations. Given the critical role SharePoint plays in many organizations, ensuring that this vulnerability is addressed promptly is crucial for maintaining the security and integrity of the supply chain.
What questions should TPRM professionals ask vendors about the RCE Vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint?
- Have you applied the latest security updates for Microsoft SharePoint to mitigate CVE-2024-38094, including updating to version/build numbers 16.0.17328.20424 for SharePoint Server Subscription Edition (SE), 16.0.10412.20001 for SharePoint Server 2019, or 16.0.5456.1000 for SharePoint Enterprise Server 2016?
- What specific configurations or policies have you implemented to safeguard your SharePoint systems against CVE-2024-38094 following the update?
- Which tools and methods do you use to continuously monitor your SharePoint environment for signs of exploitation related to CVE-2024-38094, and how do you respond to potential threats?
- How have you enhanced the security of your SharePoint servers with strong passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and access restrictions?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors subject to this risk
To address the risks associated with CVE-2024-38094, vendors should take the following actions:
- Ensure that SharePoint systems are updated to version/build numbers 16.0.17328.20424 for SharePoint Server Subscription Edition (SE), 16.0.10412.20001 for SharePoint Server 2019, and 16.0.5456.1000 for SharePoint Enterprise Server 2016, or later.
- Implement strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA). These measures provide an additional layer of security and prevent unauthorized access.
- Regularly monitor network traffic for unusual activities. Use intrusion detection systems (IDS) to identify and respond to suspicious activities promptly.
- Limit access to SharePoint servers. Configure firewalls and network segmentation to reduce the attack surface.
- Ensure that all critical data is regularly backed up. Secure backup processes help in quick recovery in case of an incident.
How TPRM professionals can leverage Black Kite for this vulnerability
Black Kite helps TPRM professionals determine which vendors are affected by CVE-2024-38094. The FocusTag provides critical asset information, such as IP addresses and subdomains, that pose risks associated with this vulnerability. This targeted intelligence allows TPRM professionals to prioritize their efforts and effectively manage the risk within their supply chain.
Black Kite published the FocusTag for CVE-2024-38094 on July 11, 2024. By leveraging this FocusTag, TPRM professionals can quickly identify at-risk vendors and take appropriate actions to mitigate the impact of this vulnerability.

CVE-2024-6235 & CVE-2024-6236: Information Disclosure & Denial of Service Vulnerability in Citrix NetScaler
What is the Information Disclosure & Denial of Service (DoS) Vulnerabilities in Citrix NetScaler?
CVE-2024-6235 is a critical vulnerability in the NetScaler Console (formerly known as NetScaler ADM). This flaw, rated with a CVSS v4.0 score of 9.4, results from improper authentication (CWE-287), enabling attackers to gain unauthorized access to confidential data. This could expose sensitive assets such as trade secrets, customer information, and other critical data.
The vulnerability affects several versions of NetScaler Console, specifically:
- NetScaler Console 14.1 before 14.1-25.53
CVE-2024-6236 also affects NetScaler SVM and NetScaler Agent in similar version ranges. Notably, the issue is most critical for instances where the NetScaler Console IP is exposed to the public internet. Citrix strongly recommends that users update to the latest versions to mitigate this risk (Citrix Support).
Additionally, Citrix discovered another related vulnerability, CVE-2024-6236, which has a CVSS v4.0 score of 7.1 and could lead to denial-of-service (DoS) attacks if exploited. This underscores the importance of timely updates and adherence to best practices, including avoiding the exposure of the NetScaler Console to the public internet (NetScaler).
The following supported versions of NetScaler Console, NetScaler Agent and NetScaler SDX (SVM) are affected by CVE-2024-6236:
- NetScaler Console 14.1 before 14.1-25.53
- NetScaler Console 13.1 before 13.1-53.22
- NetScaler Console 13.0 before 13.0-92.31
- NetScaler SDX (SVM) 14.1 before 14.1-25.53
- NetScaler SDX (SVM) 13.1 before 13.1-53.17
- NetScaler SDX (SVM) 13.0 before 13.0-92.31
- NetScaler Agent 14.1 before 14.1-25.53
- NetScaler Agent 13.1 before 13.1-53.22
- NetScaler Agent 13.0 before 13.0-92.31
For more detailed information and to apply the necessary updates, users can refer to the official Citrix security bulletin(Citrix Support) (NHS England Digital).
CVE-2024-6236 is a high-severity vulnerability affecting the NetScaler Console, NetScaler SVM, and NetScaler Agent. This vulnerability allows attackers to disrupt the normal operation of NetScaler services, leading to downtime and potential financial losses for affected organizations. The flaw arises from improper restriction of operations within the bounds of a memory buffer, making it possible for an attacker with access to a NetScaler Console, NetScaler Agent, or SVM IP to launch denial-of-service attacks. The vulnerability is classified as Denial of Service with a CVSS score of 7.1 and an EPSS score of 0.04%.
While the PoC exploit code has not yet been published, and the vulnerability has not been listed in CISA’s KEV catalog, its critical nature and the availability of exploit code make it a significant threat. Citrix products are closely monitored by threat actors, making it crucial for organizations to be proactive in addressing this vulnerability.
Why should TPRM professionals care about the Denial of Service Vulnerability in Citrix NetScaler?
TPRM professionals should be concerned about CVE-2024-6235, and CVE-2024-6236 because it can significantly disrupt the operations of organizations using Citrix NetScaler products. Exploitation of this vulnerability can lead to service disruptions, operational downtime, and potential financial losses. Ensuring that vendors address this vulnerability promptly is essential for maintaining the continuity and reliability of services provided through Citrix NetScaler products.
What questions should TPRM professionals ask vendors about the Denial of Service Vulnerability in Citrix NetScaler?
- Have you applied the necessary updates to address CVE-2024-6235 and CVE-2024-6236 across your Citrix NetScaler systems? Can you confirm the specific versions now in use for NetScaler Console, NetScaler SDX (SVM), and NetScaler Agent?
- What specific configurations or access controls have you implemented to mitigate the risks associated with CVE-2024-6235 and CVE-2024-6236, particularly concerning unauthorized access and denial-of-service attacks?
- What measures are in place to monitor and detect any unusual activities related to this vulnerability?
- How are you ensuring secure access to the administrative console, such as implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and restricting access to trusted IP addresses?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors subject to this risk
To address the risks associated with CVE-2024-6235, and CVE-2024-6236, vendors should take the following actions:
- Upgrade to the latest version: Ensure that NetScaler systems are updated to the specified versions or later.
- Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA): This enhances security for accessing the administrative console.
- Limit network access to the administrative interface: Restrict access to trusted IP addresses only, reducing the attack surface.
- Monitor network traffic for unusual activities: Use intrusion detection systems (IDS) to identify and respond promptly to any signs of exploitation attempts.
How TPRM professionals can leverage Black Kite for this vulnerability
Black Kite helps TPRM professionals determine which vendors are affected by CVE-2024-6235, and CVE-2024-6236. The FocusTag provides critical asset information, such as IP addresses and subdomains, that pose risks associated with this vulnerability. This targeted intelligence allows TPRM professionals to prioritize their efforts and effectively manage the risk within their supply chain.
Black Kite published the FocusTag for CVE-2024-6235, and CVE-2024-6236 on July 12, 2024. By leveraging this FocusTag, TPRM professionals can quickly identify at-risk vendors and take appropriate actions to mitigate the impact of this vulnerability.

CVE-2024-4879 and CVE-2024-5217: Critical Vulnerabilities in ServiceNow
What are the Critical Vulnerabilities in ServiceNow?
ServiceNow has identified multiple critical vulnerabilities that could expose businesses to remote code extension (RCE) and data breaches. These vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-4879 and CVE-2024-5217, exist due to improper input validation and inadequate access controls within certain ServiceNow modules. Exploitation of these vulnerabilities can lead to unauthorized access, data theft, and potentially severe disruptions to business operations.
CVE-2024-4879 is a critical input validation vulnerability in the ServiceNow platform. This vulnerability can be exploited by sending specially crafted requests to the vulnerable module, leading to arbitrary code execution with elevated privileges. It has a CVSS score of 9.3. Successful exploitation can result in full control over the affected system, allowing attackers to install malicious software, steal sensitive data, and disrupt services.
CVE-2024-5217 is another critical vulnerability arising from inadequate access controls in ServiceNow’s application interface. This flaw allows unauthorized users to access and manipulate sensitive information, bypassing security protocols. With a CVSS score of 9.2, attackers can exploit this vulnerability to gain access to confidential data, modify records, and potentially leak sensitive business information.
Although PoC exploit code has not yet been published, the critical nature and the potential for exploitation make these vulnerabilities significant threats. These vulnerabilities are not yet listed in CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, but given the threat landscape, it is essential to remain vigilant.
Why should TPRM professionals care about the Critical Vulnerabilities in ServiceNow?
TPRM professionals should be highly concerned about these vulnerabilities because they affect a widely used enterprise platform for IT service management. Exploiting these vulnerabilities can lead to severe consequences, including data breaches, unauthorized access to sensitive information, and significant disruptions to business operations. Ensuring that vendors address these vulnerabilities is crucial for maintaining the security and integrity of the supply chain.
What questions should TPRM professionals ask vendors about the Critical Vulnerabilities in ServiceNow?
- Have you applied the latest updates to your ServiceNow platform to address CVE-2024-4879 and CVE-2024-5217?
- What specific measures have you implemented to mitigate CVE-2024-4879 and CVE-2024-5217, particularly regarding input validation within the affected modules?
- How do you monitor and detect unauthorized access attempts or anomalies related to CVE-2024-5217 and CVE-2024-4879?
- How are you ensuring secure access control policies and implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors subject to this risk
To address the risks associated with CVE-2024-4879, and CVE-2024-5217, vendors should take the following actions:
- Ensure that ServiceNow instances are updated to the latest version and apply all patches.
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure only authorized users have access to sensitive data.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA). Enhance security for all user accounts.
- Monitor system logs for unusual activities. Regularly check for suspicious behavior and investigate anomalies immediately.
- Conduct periodic security audits. Identify and fix security gaps or misconfigurations.
How TPRM professionals can leverage Black Kite for these vulnerabilities
Black Kite helps TPRM professionals determine which vendors are affected by CVE-2024-4879, and CVE-2024-5217. The FocusTag provides critical asset information, such as IP addresses and subdomains, that pose risks associated with these vulnerabilities. This targeted intelligence allows TPRM professionals to prioritize their efforts and effectively manage the risk within their supply chain.
Black Kite published the FocusTag for these vulnerabilities on July 12, 2024. By leveraging this FocusTag, TPRM professionals can quickly identify at-risk vendors and take appropriate actions to mitigate the impact of these vulnerabilities.

CVE-2024-39929: Security Restriction Bypass Vulnerability in Exim Mail Servers
What is the Security Restriction Bypass Vulnerability in Exim Mail Servers?
CVE-2024-39929 is a critical security restriction bypass vulnerability in Exim mail servers. This vulnerability allows attackers to bypass security measures, potentially compromising the email system. The vulnerability arises from improper handling of certain configuration settings within the Exim software, enabling attackers to send specially crafted email commands that bypass security filters. This can result in unauthorized access, email manipulation, and other malicious activities.
The improper handling involves the local_scan() function in Exim’s configuration, allowing attackers to inject and execute arbitrary commands. The vulnerability exists due to inadequate sanitization of inputs passed to the local_scan() function, which fails to properly handle certain malformed input. This enables attackers to circumvent security policies configured by the administrator. The impact includes unauthorized email access and manipulation, data leakage, and potential system compromise, as attackers can gain access to sensitive email data, modify or delete emails, and potentially send malicious emails from compromised accounts.
This vulnerability is critical, with a CVSS score of 9.1. It affects all versions of Exim prior to 4.98. Although the PoC exploit is available, there are currently no known active exploitations. The vulnerability has not yet been listed in CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, but its critical nature and the availability of exploit code make it a significant threat.
Why should TPRM professionals care about the Security Restriction Bypass Vulnerability in Exim Mail Servers?
TPRM professionals should be highly concerned about this vulnerability because Exim is a widely used mail transfer agent (MTA) software, with around 15 million mail servers globally potentially affected. Exploitation of this vulnerability can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive email data, manipulation or deletion of emails, and the ability to send malicious emails from compromised accounts. Ensuring that vendors address this vulnerability is crucial for maintaining the security and integrity of the email communication systems within the supply chain.
What questions should TPRM professionals ask vendors about the Security Restriction Bypass Vulnerability in Exim Mail Servers?
- Have you updated your Exim mail servers to version 4.98 or later to address CVE-2024-39929?
- What specific configurations and security policies have you implemented to ensure the local_scan() function is properly secured against this vulnerability?
- What monitoring and detection mechanisms do you have in place to identify any unusual or suspicious activity related to CVE-2024-39929?
- How are you ensuring the security of email communications, such as implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and enabling strict access controls?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors subject to this risk
To address the risks associated with CVE-2024-39929, vendors should take the following actions:
- Update to the latest version. Ensure that Exim systems are updated to version 4.98 or later.
- Implement strict access controls. Monitor email server logs for any unusual activity.
- Ensure proper security configurations. Regularly audit configurations to identify any potential misconfigurations.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA): Enhance security for all accounts.
- Monitor network traffic for unusual activities: Use intrusion detection systems (IDS) to identify and respond promptly to any signs of exploitation attempts.
How TPRM professionals can leverage Black Kite for this vulnerability
Black Kite helps TPRM professionals determine which vendors are affected by CVE-2024-39929. The FocusTag provides critical asset information, such as IP addresses and subdomains, that pose risks associated with this vulnerability. This targeted intelligence allows TPRM professionals to prioritize their efforts and effectively manage the risk within their supply chain.
Black Kite published the FocusTag for CVE-2024-39929 on July 15, 2024. By leveraging this FocusTag, TPRM professionals can quickly identify at-risk vendors and take appropriate actions to mitigate the impact of this vulnerability.

CVE-2024-36401: Eval Injection and RCE Vulnerability in GeoServer
What is the Eval Injection and RCE Vulnerability in GeoServer?
CVE-2024-36401 is a critical remote code extension (RCE) vulnerability affecting GeoServer, an open-source server for sharing geospatial data. This vulnerability is caused by improper neutralization of directives in dynamically evaluated code. It allows unauthenticated attackers to perform RCE by sending specially crafted input that is unsafely evaluated as XPath expressions. The flaw can be exploited by attackers to execute arbitrary commands on the affected system with the privileges of the GeoServer service, potentially leading to full server compromise.
This vulnerability is classified as critical, with a CVSS score of 9.8 and an EPSS score of 78.35%. It can be exploited by unauthenticated attackers, significantly increasing the attack surface. The vulnerability stems from how GeoServer evaluates property names within geospatial data, inadvertently allowing malicious input to trigger code execution.
The proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code was publicly disclosed on July 8, 2024, increasing the risk of exploitation by malicious actors. The vulnerability has been listed in CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog on July 15, 2024, and is under active attack. The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has issued an urgent warning about this flaw, emphasizing its active exploitation by malicious actors.
Why should TPRM professionals care about the Eval Injection and RCE Vulnerability in GeoServer?
TPRM professionals should be highly concerned about this vulnerability because it affects a critical system for sharing geospatial data. Exploitation of this vulnerability can lead to unauthorized access and control of the GeoServer host, resulting in potential data breaches, system manipulation, and significant disruptions to business operations. Ensuring that vendors address this vulnerability is crucial for maintaining the security and integrity of geospatial data systems within the supply chain.
What questions should TPRM professionals ask vendors about the Eval Injection and RCE Vulnerability in GeoServer?
- Have you updated your GeoServer systems to the latest versions (2.25.2, 2.24.4, or 2.23.6) to address CVE-2024-36401?
- What specific measures have you implemented to ensure the proper neutralization of directives in dynamically evaluated code, particularly within XPath expressions, to mitigate CVE-2024-36401?
- How are you monitoring your GeoServer environment for signs of exploitation related to CVE-2024-36401?
- What access controls and security measures have you implemented to protect the integrity of your geospatial data and prevent unauthorized access?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors subject to this risk
To address the risks associated with CVE-2024-36401, vendors should take the following actions:
- Update to the latest version. Immediately update GeoServer to versions 2.25.2, 2.24.4, or 2.23.6, where this vulnerability has been patched. Check the GitHub repository for details.
- Temporary mitigation: If immediate patching is not possible, temporarily mitigate the vulnerability by removing the “gt-complex-x.y.jar” file from the GeoServer installation. Note that this may disrupt some complex feature functionalities.
- Implement strong access controls. Regularly monitor network traffic to detect and respond to suspicious activities.
- Deploy web application firewalls (WAF). Filter and monitor HTTP requests to and from the GeoServer instance, providing an additional layer of security.
- Ensure regular backups. Verify the integrity of backups to facilitate quick recovery in the event of a breach.
- Continuously monitor for any unusual activities.
How TPRM professionals can leverage Black Kite for this vulnerability
Black Kite helps TPRM professionals determine which vendors are affected by CVE-2024-36401. The FocusTag provides critical asset information, such as IP addresses and subdomains, that pose risks associated with this vulnerability. This targeted intelligence allows TPRM professionals to prioritize their efforts and effectively manage the risk within their supply chain.
Black Kite published the FocusTag for CVE-2024-36401 on July 16, 2024. By leveraging this FocusTag, TPRM professionals can quickly identify at-risk vendors and take appropriate actions to mitigate the impact of this vulnerability.

ENHANCING TPRM STRATEGIES WITH BLACK KITE’S FOCUSTAGS™
In today’s rapidly evolving cyber threat landscape, staying ahead of vulnerabilities is imperative for robust Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM). Black Kite’s FocusTags™ are at the forefront of this challenge, providing essential insights and tools to effectively manage these risks. The value of these tags becomes evident when faced with critical vulnerabilities like those in Serv-U FTP, Microsoft SharePoint, Citrix NetScaler, ServiceNow, Exim Mail, and GeoServer. Here’s how Black Kite’s FocusTags™ transform TPRM practices:
- Real-Time Vulnerability Tracking: Instantly identifying vendors affected by the latest vulnerabilities allows for a swift and strategic response.
- Risk Prioritization: By evaluating both vendor importance and vulnerability severity, FocusTags™ help in allocating resources more effectively.
- Informed Vendor Conversations: Facilitate targeted discussions with vendors, focusing on their specific security posture in relation to the identified vulnerabilities.
- Comprehensive Security Overview: With a broad view of the threat landscape, these tags aid in enhancing overall cybersecurity strategies.
Black Kite’s FocusTags™, especially when dealing with the complexities of recent vulnerabilities in diverse systems, offer a streamlined, intelligent approach to TPRM, converting intricate cyber threat data into actionable intelligence. This capability is critical for managing risks efficiently and proactively in an environment where cyber threats are constantly evolving.
By leveraging Black Kite’s FocusTags™, TPRM professionals can enhance their risk management strategies, ensuring a more secure and resilient supply chain in the face of evolving cyber threats.
we are currently working on a FocusTags™ for Crowdstrike and will have that pushed live eminently. Please check back for an update
About Focus Friday
Every week, we delve into the realms of critical vulnerabilities and their implications from a Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) perspective. This series is dedicated to shedding light on pressing cybersecurity threats, offering in-depth analyses, and providing actionable insights.
FocusTagsTM in the Last 30 Days:
- Serv-U FTP: CVE-2024-28995, Directory Traversal Vulnerability in SolarWinds Serv-U.
- Microsoft SharePoint: CVE-2024-38094, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint.
- Citrix NetScaler: CVE-2024-6235, Information Disclosure Vulnerability in Citrix NetScaler.
- ServiceNow: CVE-2024-4879, Input Validation Vulnerability in ServiceNow.
- Exim Mail: CVE-2024-39929, Security Restriction Bypass Vulnerability in Exim Mail Servers.
- GeoServer: CVE-2024-36401, Eval Injection and RCE Vulnerability in GeoServer.
- PHP-CGI: CVE-2024-4577, OS Command Injection Vulnerability in PHP-CGI Module.
- Microsoft MSMQ: CVE-2024-30080, Use After Free, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ).
- Rejetto HFS: CVE-2024-23692, Template Injection Vulnerability, Unauthenticated RCE Vulnerability in Rejetto HTTP File Server
- Checkpoint SNX: CVE-2024-24919, An Information Disclosure Vulnerability in Check Point’s CloudGuard Network, Quantum Maestro, Quantum Scalable Chassis, Quantum Security Gateways, Quantum Spark Appliances
- DNSBomb: CVE-2023-28450, DNSBomb Attack in Dnsmasq, CoreDNS, Knot DNS, Simple DNS Plus, Technitium DNS, MaraDNS, CoreDNS
- Veeam VBEM: CVE-2024-29849, Authentication Bypass Vulnerability in Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager
References:
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-28995
https://www.labs.greynoise.io/grimoire/2024-06-solarwinds-serv-u
https://attackerkb.com/topics/2k7UrkHyl3/cve-2024-28995/rapid7-analysis#
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-38094
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-38023
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-38024
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability/CVE-2024-38094
https://github.com/testanull/MS-SharePoint-July-Patch-RCE-PoC/tree/main
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-6235
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-6236
https://duo.com/decipher/citrix-warns-of-critical-netscaler-console-flaw
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-39929
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-4879
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-5217
https://support.servicenow.com/kb?id=kb_article_view&sysparm_article=KB1648313
https://bugs.exim.org/show_bug.cgi?id=3099#c4
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-36401
https://github.com/geoserver/geoserver/security/advisories/GHSA-6jj6-gm7p-fcvv
https://github.com/geotools/geotools/security/advisories/GHSA-w3pj-wh35-fq8w
https://www.vicarius.io/vsociety/posts/geoserver-rce-cve-2024-36401

