FOCUS FRIDAY: Addressing the Mirth Connect and Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager Vulnerabilities: A TPRM Approach
Written by: Ferdi GülAdditional Contributions: Ferhat Dikbiyik
Welcome to this week’s Focus Friday, where we delve into critical vulnerabilities that are reshaping Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) practices. Today, we spotlight two high-profile issues: NextGen’s Healthcare Mirth Connect and Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager incidents. Our discussion will not only cover the specifics of these incidents but also illustrate how Black Kite’s FocusTags™ can drive proactive risk management strategies.

CVE-2023-43208 in NextGen Healthcare Mirth Connect: A TPRM Perspective
What is the CVE-2023-43208 vulnerability?
The healthcare solution known as NextGen Healthcare Mirth Connect, previously known as Nextgen or MirthConnect, is closely integrated with EDI systems. It provides two-way communication among different health information systems, ensuring secure patient data exchange across various medical software platforms used by hospitals and clinics. CVE-2023-43208 is a critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability discovered in NextGen Healthcare’s Mirth Connect. This flaw allows attackers to remotely control unpatched systems without requiring credentials. Since Mirth Connect often manages sensitive healthcare data, this vulnerability poses a significant security threat. Proof of concept exploit code for CVE-2023-43208 was published on January 31, 2024, and the vulnerability was added to CISA’s KEV catalog on May 20, 2024, due to recent exploitation by the threat actors. Disclosed in late 2023, this critical vulnerability requires immediate patching due to its severity and the number of affected systems.
Technical Details
This flaw allows attackers to remotely seize control of vulnerable systems by sending specially crafted data packets. The issue’s root is Mirth Connect’s improper handling of deserialized data, which can be exploited to execute arbitrary operating system commands via specially crafted HTTP requests. This vulnerability emerged after an incomplete fix for CVE-2023-37679.
The severity of this issue is underscored by its critical CVSS score of 9.8, and EPSS score is 94.57%. Exploiting this vulnerability could have disastrous consequences, especially considering the sensitivity of healthcare data managed by Mirth Connect. A successful attack could grant initial access to networks, potentially leading to widespread data breaches and jeopardizing patient privacy. The number of ransomware attacks targeting the healthcare industry has been increasing, as indicated by our latest ransomware report. The industry is still recovering from the ransomware attacks, particularly those against Change Healthcare.When we examine the exploit code of the vulnerability, it is understood that it causes RCE by leveraging the application’s insecure handling of deserialized data. We can group the exploit code under three main headings:
- Verification for Mirth Connect: The exploit code ensures it’s interfacing with a Mirth Connect instance by retrieving and scrutinizing the version details to ascertain if it falls within the susceptible range (≤ 4.4.0).
- Selection of Exploit Based on Version:
– CVE-2023-37679 Exploit (≤ 4.3.0): This targets the original vulnerability found in older versions by employing a malicious XML payload to execute commands through a ProcessBuilder object.
– CVE-2023-43208 Exploit (≤ 4.4.0): It exploits the incomplete fix for CVE-2023-37679, utilizing a chained transformer method from the Apache Commons Collections library to execute code. - Execution of Commands: Both exploit methods endeavor to execute commands provided by the attacker on the target system, potentially resulting in the installation of malware, theft of data, or compromise of the system’s integrity.
What is the scope of CVE-2023-43208?
This vulnerability specifically impacts NextGen Healthcare’s Mirth Connect versions prior to the latest patched version, 4.4.1.
The potential consequences of CVE-2023-43208 include data breaches and deployment of ransomware leading to privacy violations and identity theft, disruption of healthcare services, and significant financial losses due to fines, legal costs, and reputational damage.
How many endpoints can be accessed through Mirth Connect?
Recent research indicates that over 600 endpoints may be accessible externally via Mirth Connect. It’s important to note that this number may not account for endpoints relying solely on other Mirth Connect access methods.
Timeline for CVE-2023-43208:
October 25, 2023 (Wednesday)
- The vulnerability has started to be shared as an announcement on some websites.
October 26, 2023 (Thursday)
- The vulnerability was disclosed on NVD (National Vulnerability Database). NVD modified the vulnerability details on May 23, 2024.
January 31, 2024 (Wednesday)
- The exploit code, which includes the Metasploit module, was published publicly.
May 20, 2024 (Monday)
- The vulnerability was analyzed and the FocusTagTM processing was completed by Black Kite’s Research Team.
- The vulnerability was listed on CISA’s KEV catalog.
TPRM Implications
The top priority for TPRM teams is to address the critical vulnerability CVE-2023-43208. This vulnerability, found in Mirth Connect, is an RCE flaw in the healthcare data integration platform, which exposes sensitive patient information to cybercriminals. A successful attack would enable attackers to steal, modify, or delete critical information, particularly emphasizing the severity of such actions in the context of medical records.
To mitigate the risk associated with CVE-2023-43208, TPRM professionals should follow these steps:
- Perform an inventory review to confirm the existence and status of all installed Mirth Connect deployments managed by third-party providers within your healthcare organization’s network.
- The statement read, “Proactively reach out to any third-party vendors (for example, others using Mirth Connect) to make them aware of the vulnerability and determine if your system is impacted for patching.
- Expand monitoring programs for illicit activity on healthcare data systems.
Engaging with Vendors Regarding CVE-2023-43208
A big drawback of NextGen Healthcare Mirth Connect is that it has CVE-2023-43208, thus you need to contact your vendors. The following are some of the things you might want to know:
- Did NextGen Healthcare develop patches for the affected Mirth Connect versions against CVE-2023-43208?
- Do you have an MSP for Mirth Connect? If yes, have they fixed the bugs or set up a patch update timetable?
- Regarding your suppliers’ infrastructures, how do their monitoring processes ensure no potential exploits from CVE-2023-43208 can occur?
- What else are your vendors doing besides applying patches to reduce risks posed by CVE-2023-43208?
Conversing with sellers can help us comprehend how they deal with this critical defect. Then, we can make our choices about Mirth Connect security based on accurate information.
How can vendors detect and remediate CVE-2023-43208?
Nextgen has released some patches to address this critical security vulnerability. Here are some proactive measures vendors can take:
- Review Mirth Connect Version: Find out the current Mirth Connect version. If it is below 4.4.1, your system could be vulnerable. To check if your Mirth Connect instance is vulnerable, use the following curl command:
$ curl -k -H ‘X-Requested-With: OpenAPI’ https://<server>:<port>/api/server/version
If the version returned is 4.4.0 and earlier, it is vulnerable.
- Patch Application: Make sure that you have updated Mirth Connect to version 4.4.1 or above; Apply this patch to correct CVE-2023-43208 vulnerability; please refer to official NextGen Healthcare documentation for upgrade instructions.
- Disable Management Interface: If immediate patching is not possible, consider disabling remote access to the Mirth Connect management interface as a temporary measure that decreases the attack surface.
- Restrict Access: Just allow authorized individuals and trusted IP addresses into the Mirth Connect server.
- Monitor Network Activity: Security solutions should be put in place so that network activities can constantly be monitored for suspicious moves indicating attempts of exploitation.
- Maintain Backups: Regularly, back up your Mirth Connect configuration files and keep these backups in a safe place away from your Mirth Connect server itself so that if an attacker succeeds in compromising one or more configurations, recovery may be faster.
This way, companies can effectively mitigate risks associated with CVE-2023-43208 and secure their systems against unauthorized access and potential data loss.
Mitigating Vendor Risk of CVE-2023-43208 with Black Kite’s FocusTags™
On May 20, 2024, the Black Kite platform disclosed a critical vulnerability identified as CVE-2023-43208. Organizations need to prioritize robust security practices as a reminder. Considering the importance of NextGen’s Healthcare Mirth Connect in data backup and recovery during emergencies, it’s crucial not to leave this critical infrastructure vulnerable.

to assess and prioritize risks diligently, fortifying their defenses effectively.
CVE-2024-29849 in Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager (VBEM): A TPRM Perspective
What is the CVE-2024-29849 vulnerability?
Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager (VBEM) is a management console created for Veeam Backup & Replication, a popular data backup and restore solution. VBEM offers a centralized web interface to manage your backups across the infrastructure of your entire organization.
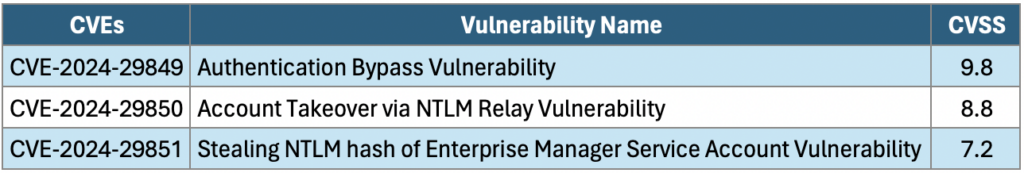
The recent critical vulnerability (CVE-2024-29849) has been found in VBEM, enabling an attacker to take over user accounts potentially. CVE-2024-29849 is a Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager vulnerability that allows an attacker to bypass authentication and log in to the VBEM web interface as any user. It may allow the attacker full control over the backup and replication management system. The severity of this vulnerability is rated 9.8 by the CVSS, which means it is critical in the wild. Ensure that the most recent patches are installed to address the issue.
There have been no reports of active exploitation in the wild. Still, some cybercriminal groups, such as Cuba ransomware and FIN7, have targeted Veeam’s platforms before, using similar vulnerabilities to encrypt data and conduct extortion activities. This vulnerability may open the door for the exploitation of threat actors.
What is the scope of CVE-2024-29849?
The scope of the vulnerability CVE-2024-29849 is strictly narrowed to Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager versions, which are older than the latest version with a released patch.
An attacker could use this vulnerability to gain unauthorized access to VBEM and perform some action with the privileges of the compromised account. The following actions might include:
- Take over user accounts, such as administrators.
- The jobs fail; the strategy of data protection is in danger.
- Find an entry point into your network.
- Thus, it prevents this critical vulnerability and applies all the very latest patches from Veeam.
The affected products include 5.0, 6.1, 6.5, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0, 9.5, 10, 11, 12, and 12.1. The fixed version is 12.1.2.172.
Timeline for Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager Vulnerability:
May 21, 2024 (Tuesday)
- Veeam likely becomes aware of the vulnerability and starts working on a fix.
May 22, 2024 (Wednesday)
- The vulnerability is publicly published on NVD and assigned the CVE-ID CVE-2024-29849.
- Veeam will likely release details of the vulnerability, including technical specifics and a patch (KB4581). Security agencies and news outlets may also report on it around this time.
The vulnerability was analyzed, and Black Kite’s Research Team completed the FocusTagTM processing.
TPRM Implications
What course of action TPRM professionals take is paramount. This vulnerability will allow unauthorized users to access the VBEM web interface, possibly compromising your backups and virtual machines. Unauthorized backup access can be catastrophic because hackers might tamper with or delete critical data.
- Create an inventory to find all Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager deployments from within the enterprise, including third-party vendors who use them.
- Ensure all identified VBEM instances are updated to the latest KB4581 version to address CVE-2024-29849. Prioritize the patching of the most vulnerable systems to reduce the window in which they could be exploited.
- Contact all third-party vendors who manage VBEM on behalf of your organization and alert them to CVE-2024-29849. Engage with them to ensure the VBEM deployments are updated quickly.
- Extend current monitoring programs to watch suspicious activity targeting healthcare data systems to note the existence of suspicious activity. An increased level of awareness will enable the identification of attempts to exploit CVE-2024-29849 and allow a swift response.
These are TPRM best practices, which help place organizations in a very good position to mitigate the risks correctly posed by the recently identified vulnerability, namely, CVE-2024-29849, and secure the critical backup infrastructure. This is proactive and will ensure a powerful and resilient defense against such potential future vulnerabilities, promising a high level of assurance of cybersecurity posture.
Engaging with Vendors
This guide provides a set of questions for discussion with Veeam on the topic of CVE-2024-29849, a critical vulnerability in Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager (VBEM). You should get a better view of the exploit and Veeam’s response strategy by raising these questions:
- How does CVE-2024-29849 allow unauthorized access to the VBEM web interface?
- Can any unauthenticated user exploit this, or does it require certain user privileges?
- Can a remote attacker attack CVE-2024-29849, or does the VBEM system need to be accessed physically?
- Are there any specific logs or indicators in the system that might show an attempt to exploit CVE-2024-29849?
- While patching is a must, what interim measures can administrators take to reduce the risk associated with CVE-2024-29849? For example, would it be safe to temporarily disable VBEM if it’s not crucial?
- How critical is it that organizations update to the patched version, KB4581, to mitigate CVE-2024-29849?
These questions will provide you with more details from Veeam regarding the technical details of the CVE-2024-29849 vulnerability and their remediation approach. Such proactive engagement enables you to make the right decisions.
How can vendors detect and remediate CVE-2024-29849?
There are some general code auditing practices:
- Focus on sections where user input is processed, particularly in the VBEM web interface.
- Apply the official patch from Veeam, version 12.1.2.172, for critical security fixes.
- Limit access to the VBEM web interface only to authorized users.
- VBEM deployment is optional; if not installed, these vulnerabilities don’t affect your environment. Check for VBEM installation by running a specific PowerShell command on the Veeam Backup Server:
- You can choose whether or not to deploy VBEM; if it’s not installed, your system won’t be vulnerable. To confirm VBEM installation, execute a particular PowerShell command on the Veeam Backup Server:
$ Get-VBRServer | Out-Null [Veeam.Backup.Core.SBackupOptions]::GetEnterpriseServerInfo() | Format-List
- If immediate upgrading isn’t possible, users can mitigate the risk by halting and disabling both the ‘VeeamEnterpriseManagerSvc’ and the ‘VeeamRESTSvc’. However, it’s crucial not to interrupt the operation of the ‘Veeam Backup Server RESTful API Service’.
- Furthermore, Veeam suggests uninstalling Backup Enterprise Manager if it’s not actively utilized within your environment, as it’s considered an optional add-on application.
- Monitor Network Traffic. Keep an eye out for suspicious activity on your network.
- Subscribe to security advisories from Veeam to receive updates on future vulnerabilities.
Mitigating Vendor Risk of CVE-2024-29849 with Black Kite’s FocusTags™
On May 23, 2024, the Black Kite platform disclosed a critical vulnerability identified as CVE-2024-29849. This highlights the potential risks associated with unpatched Mirth Connect software and underscores the importance of proactive security measures to safeguard critical network infrastructure components.

Enhancing TPRM Capabilities with Black Kite’s FocusTags™
Effective Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) is crucial in today’s dynamic cybersecurity landscape. Black Kite’s FocusTags™ for NextGen’s Healthcare Mirth Connect and Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager (VBEM) specifically address the unique challenges posed by these incidents. Here’s how these tags are critical in managing third-party risks:
- Immediate Threat Identification: Rapidly pinpoints vendors affected by the Mirth Connect or the VBEM vulnerabilities, enabling swift mitigation actions.
- Risk Prioritization: Assists in categorizing vendor risks, focusing on those with the highest exposure due to these specific incidents.
- Strategic Vendor Interactions: Facilitates detailed discussions with vendors about their exposure to the Mirth Connect or the VBEM vulnerability, ensuring they understand the risks and mitigation strategies.
- Comprehensive Security Enhancement: Provides insights into the cascading impacts of the Mirth Connect or the VBEM, helping to bolster overall security posture and resilience.
With these FocusTags™, Black Kite translates intricate threat data into actionable intelligence, empowering TPRM professionals to manage and mitigate risks associated with specific high-profile incidents proactively.
Want to take a closer look at FocusTags™?
Take our platform for a test drive and request a demo today.
About Focus Friday
Every week, we delve into the realms of critical vulnerabilities and their implications from a Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) perspective. This series is dedicated to shedding light on pressing cybersecurity threats, offering in-depth analyses, and providing actionable insights.
FocusTagsTM in the Last 30 Days:
- Veeam VBEM: CVE-2024-29849, Backup Enterprise Manager Authentication Bypass Vulnerability in Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager.
- Multi Connect: CVE-2023-43208, Deserialization of Untrusted Data Vulnerability, RCE Vulnerability in NextGen Healthcare Mirth Connect.
- Cacti: CVE-2024-25641, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Cacti
- Veeam SPC: CVE-2024-29212, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Veeam Service Provider Console
- TinyProxy: CVE-2023-49606, Use-After-Free Vulnerability, RCE Vulnerability in Tinyproxy
- ArubaOS: CVE-2024-26304, Buffer Overflow Vulnerability, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in ArubaOS
- CrushFTP VFS: CVE-2024-4040, a Server Side Template Injection Vulnerability in CrushFTP
- Sisense Client
- FortiClient EMS: CVE-2023-48788, SQL Injection Vulnerability in Fortinet’s FortiClient Endpoint Management Server
- FortiOS SSL VPN: CVE-2024-21762, A Out-of-Bounds Write Vulnerability in FortiOS [Tag updated]
- Outlook RCE: CVE-2023-36439, RCE Vulnerability in Microsoft Exchange Server
- Change Healthcare Client
- JetBrains TeamCity: CVE-2023-42793, Authentication Bypass in JetBrains TeamCity CI/CD Servers; CVE-2024-27198, Authentication Bypass Vulnerability [Tag Updated]
- ScreenConnect:CVE-2024-1709, Authentication Bypass Vulnerability
- Cisco ASA [Suspected]CVE-2020-3259, Information Disclosure Vulnerability
- Exchange Server:CVE-2024-21410,Privilege Elevation Vulnerability
- QNAP QTS:CVE-2023-47218, CVE-2023-50358, OS Command Injection Vulnerability
- Symantec MG [Suspected]:CVE-2024-23615, CVE-2024-23614, Buffer Overflow Vulnerability (Remote Code Execution)
- FortiOS SSL VPN [Suspected]:CVE-2024-22024, An Out-of-Bounds Write Vulnerability
- RoundCube [Suspected] :CVE-2023-43770, Stored-XSS Vulnerability [Updated]
- Citrix ADC/Gateway:CVE-2023-6549 [Updated], Buffer Overflow Vulnerability
- Ivanti EPMM:CVE-2023-35082 [Updated], Authentication Bypass Vulnerability
- GoAnywhere [Suspected]:CVE-2024-0204, Authentication Bypass Vulnerability
- Redis RCE: CVE-2023-41056, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- Ivanti ICS: CVE-2024-21887, Command Injection Vulnerability, CVE-2023-46805, Authentication Bypass Vulnerability
References:
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2023-43208
http://packetstormsecurity.com/files/176920/Mirth-Connect-4.4.0-Remote-Command-Execution.html
https://www.meditecs.com/kb/mirth-connect-vulnerability-cve-2023-43208
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-29849
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-29850
https://thehackernews.com/2024/05/nextgen-healthcare-mirth-connect-under.html

