FOCUS FRIDAY: INSIGHTS INTO THIRD-PARTY RISKS IN FORTINET CORE PRODUCTS, CISCO RV ROUTERS, AND IVANTI CONNECT SECURE VULNERABILITIES
Welcome to this week’s Focus Friday blog, where we delve into high-profile cybersecurity incidents from a Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) perspective. This week, we examine critical vulnerabilities affecting Fortinet Core Products, Cisco RV Routers, and Ivanti Connect Secure. These vulnerabilities present significant risks, from privilege escalation to remote code execution, impacting enterprise security across various sectors. Understanding and addressing these issues are essential to maintaining a strong security posture and mitigating potential breaches.
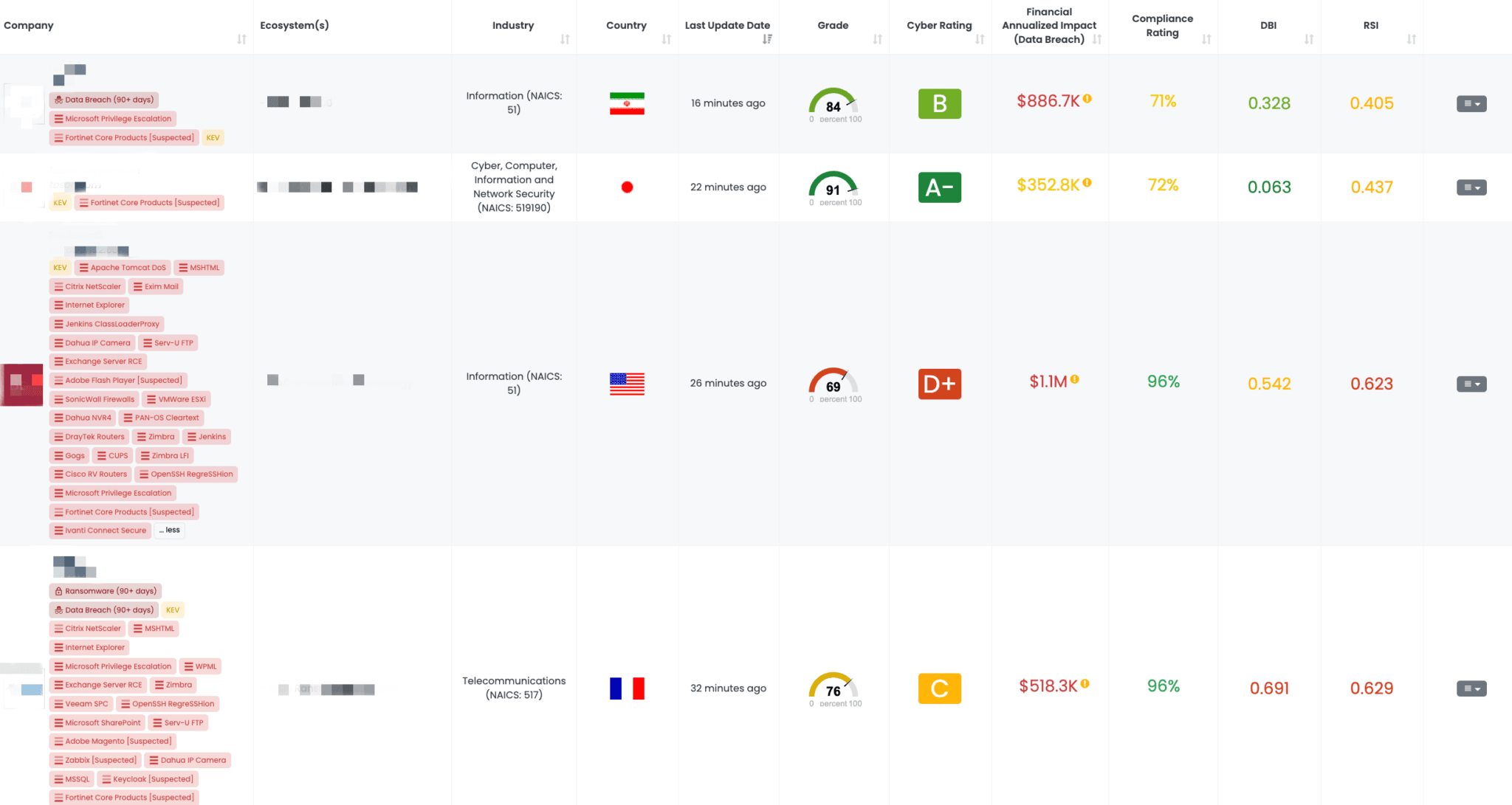
Filtered view of companies with Fortinet Core Products FocusTag™ on the Black Kite platform.
CVE-2024-23113: Fortinet Core Products Format String Vulnerability
What is the Fortinet Core Products Format String Vulnerability?
CVE-2024-23113 is a critical format string vulnerability affecting Fortinet products, including FortiOS, FortiProxy, FortiPAM, and FortiSwitchManager. This flaw allows a remote, unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code by sending specially crafted requests to the affected systems. The vulnerability, with a CVSS score of 9.8 and an EPSS score of 0.80%, was disclosed in February 2024 and added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog on October 9, 2024. Although no proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit code has been publicly released, threat actors are focusing on exploiting vulnerabilities in Fortinet systems to breach corporate networks, aiming to launch ransomware attacks or engage in cyber espionage. Therefore, it is recommended to upgrade the Fortinet’s products to the patched versions.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Care About This Vulnerability?
For TPRM professionals, vulnerabilities in Fortinet core products are highly concerning because these systems are often deployed in sensitive enterprise environments. If exploited, CVE-2024-23113 could allow attackers to take control of Fortinet systems, execute arbitrary commands, and compromise the entire network. This risk is particularly critical in environments where FortiOS is used to secure sensitive operations, including financial transactions, communications, and administrative controls. The vulnerability’s ability to bypass authentication and execute commands remotely makes it a prime target for ransomware attacks and cyber espionage.
What Questions Should TPRM Professionals Ask Vendors About This Vulnerability?
To mitigate the risk of CVE-2024-23113, TPRM professionals should ask vendors the following questions:
- Have you updated all instances of FortiOS, FortiProxy, FortiPAM, and FortiSwitchManager to the latest versions (FortiOS: 7.4.3, 7.2.7, or 7.0.14 or above, FortiProxy: 7.4.3, 7.2.9, or 7.0.16 or above, FortiSwitchManager: 7.2.4 or 7.0.4 or above) to mitigate the risk of CVE-2024-23113?
- Have you implemented the recommended action of disabling FGFM access for each interface until the system can be updated, and closely observing network activity for any abnormal behavior that may indicate attempted exploitation of this vulnerability?
- Can you confirm if you have restricted FGFM connections to specific IPs as an additional mitigation step, even though it does not fully prevent exploitation and should be treated as a temporary solution until patching is completed?
- For FortiPAM, have you migrated to fixed releases as no specific patches are provided for vulnerable versions to mitigate the risk of CVE-2024-23113?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors Subject to This Risk
Vendors using affected Fortinet products should:
- Apply patches immediately to upgrade FortiOS to versions 7.4.3, 7.2.7, or 7.0.14 and similar versions for FortiProxy and FortiSwitchManager.
- Disable FGFM access temporarily, or restrict it to specific trusted IPs to minimize exposure.
- Implement local-in policies to restrict access to FGFM services.
- Monitor network activity closely for signs of exploitation, and review access logs regularly.
How Can TPRM Professionals Leverage Black Kite for This Vulnerability?
Black Kite provides the Fortinet Core Products FocusTag to help identify vendors with potential exposure to CVE-2024-23113. The tag, first published on October 9, 2024, allows TPRM professionals to identify at-risk vendors by mapping affected assets like IP addresses and subdomains. This enables targeted risk assessments and allows professionals to prioritize outreach and remediation efforts for the most vulnerable vendors. Black Kite’s ability to provide real-time intelligence on exploited vulnerabilities is a key differentiator in managing third-party risks.
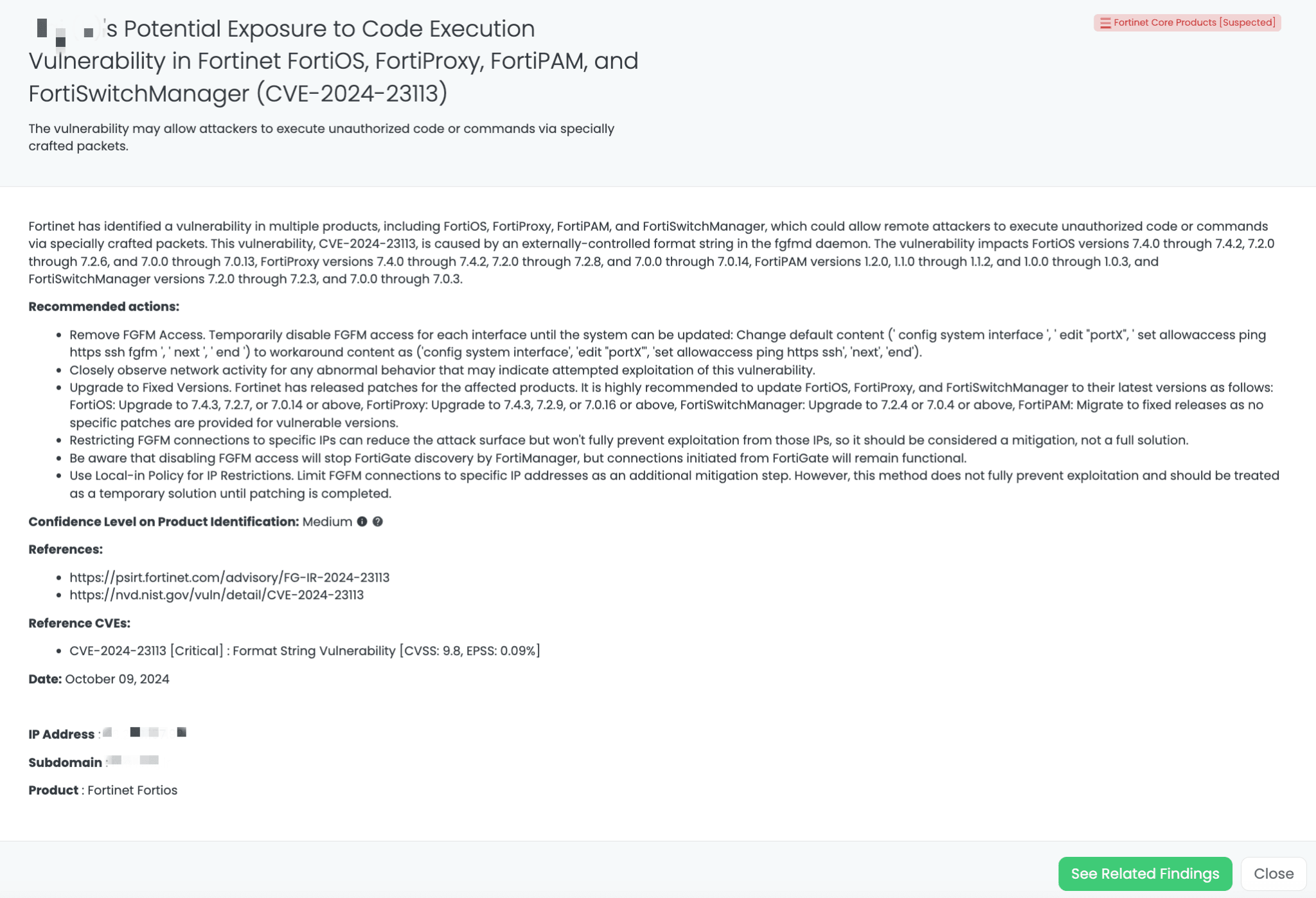
Black Kite’s Fortinet Core Products FocusTag™ details critical insights on the event for TPRM professionals.
CVE-2024-20393 and CVE-2024-20470: Cisco RV Routers Privilege Escalation and Remote Code Execution Vulnerabilities
What are the Cisco RV Routers Privilege Escalation and RCE Vulnerabilities?
CVE-2024-20393 and CVE-2024-20470 are high-severity vulnerabilities impacting Cisco RV340, RV340W, RV345, and RV345P VPN Routers. CVE-2024-20393 enables privilege escalation, while CVE-2024-20470 allows remote code execution. Both vulnerabilities involve weaknesses in the web-based management interface and can be exploited by an authenticated attacker with limited privileges. With CVSS scores of 7.2 and 8.8, respectively, these flaws pose serious risks to network integrity and sensitive data.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Care About These Vulnerabilities?
For organizations using Cisco RV routers, these vulnerabilities can severely compromise network security. If exploited, attackers can escalate privileges or execute arbitrary code, leading to unauthorized access to sensitive data or full system takeover. Given that these routers are often used in business-critical environments, failing to address these vulnerabilities may result in breaches, data exfiltration, or service disruption.
What Questions Should TPRM Professionals Ask Vendors About These Vulnerabilities?
- Have you checked and confirmed that the remote management feature is disabled on all your Cisco Small Business RV Series routers, specifically the RV340, RV340W, RV345, and RV345P models, to mitigate the risk of CVE-2024-20393 and CVE-2024-20470?
- Given that Cisco has not provided any patches or workarounds for these vulnerabilities, have you considered replacing the affected Cisco Small Business RV Series routers with more secure alternatives that receive active support and security updates?
- Can you confirm if you have implemented network monitoring solutions to detect any suspicious activity that could indicate an exploitation of the privilege escalation and remote code execution vulnerabilities (CVE-2024-20393 and CVE-2024-20470) in the Cisco Small Business RV Series routers?
- Have you taken steps to restrict network access to the affected Cisco Small Business RV Series routers to local connections only, as a measure to mitigate the risk of CVE-2024-20393 and CVE-2024-20470?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors Subject to This Risk
- Disable remote management immediately.
- Migrate to secure router models, as these devices no longer receive software support.
- Restrict network exposure to local traffic only.
- Monitor network traffic for suspicious activity related to privilege escalation or RCE attempts.
How Can TPRM Professionals Leverage Black Kite for These Vulnerabilities?
Black Kite’s Cisco RV Routers FocusTag helps TPRM professionals identify vendors at risk from these vulnerabilities. Published on October 7, 2024, the FocusTag offers real-time data on vulnerable assets, allowing organizations to prioritize mitigation efforts and reduce exposure. By providing asset-specific intelligence such as IP addresses and vulnerable systems, Black Kite enables more focused risk management.
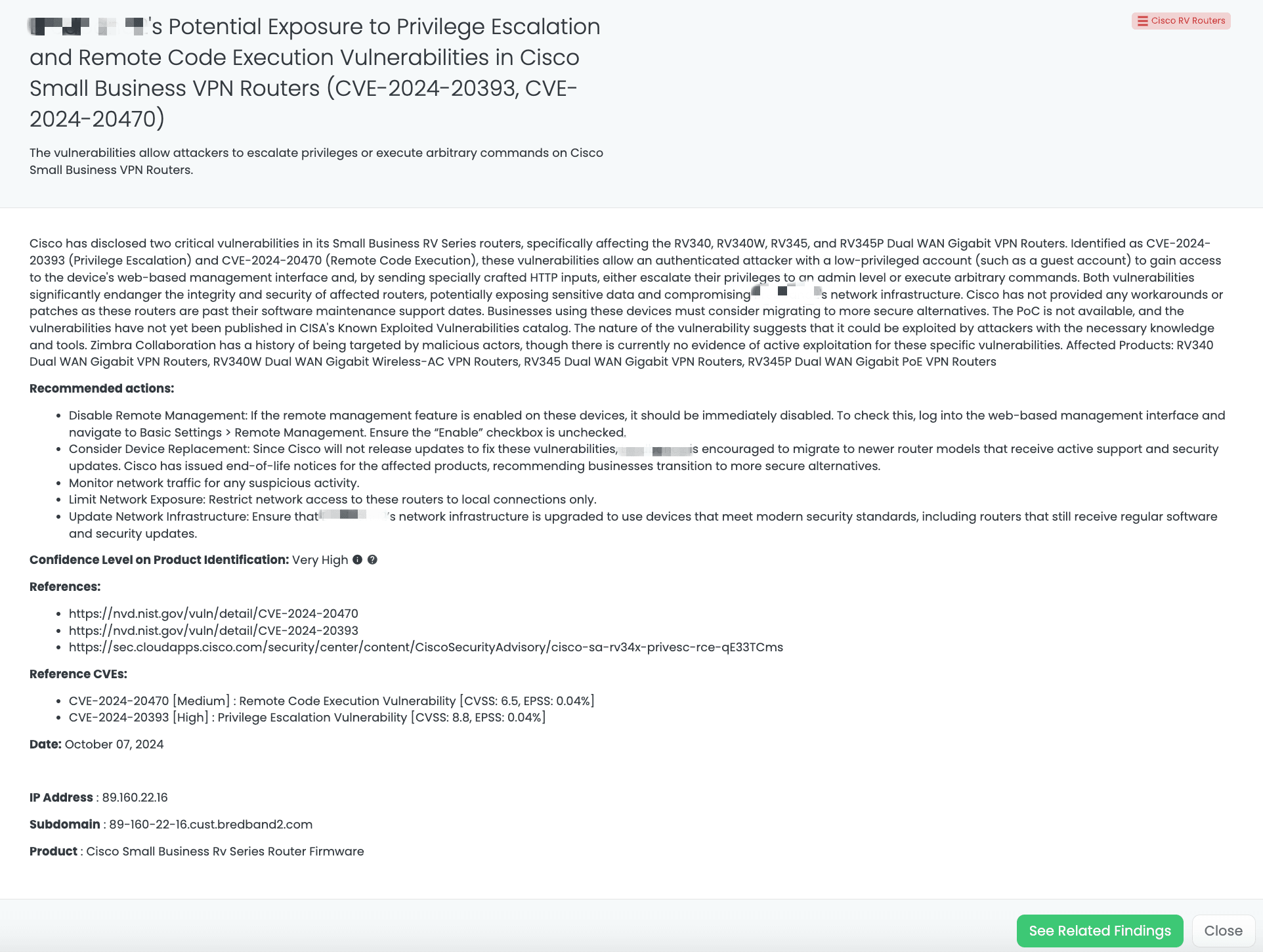
Black Kite’s Cisco RV Routers FocusTag™ details critical insights on the event for TPRM professionals.
CVE-2024-37404: Ivanti Connect Secure Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
What is the Ivanti Connect Secure RCE Vulnerability?
CVE-2024-37404 is a critical Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting Ivanti Connect Secure and Policy Secure products. This flaw, caused by improper input validation in the admin portal during the Certificate Signing Request (CSR) generation process, allows an authenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code. With a CVSS score of 9.1, this vulnerability poses a significant risk, potentially allowing attackers to take full control of vulnerable systems. The issue was first disclosed in October 2024, and while no known exploitation has been observed in the wild, a proof-of-concept (PoC) has been published, demonstrating how the attack can be carried out by manipulating configuration files through specially crafted input.
In previous discussions on ICS, we noted that the Chinese nation-state-linked threat actor UTA0178 is suspected of exploiting these systems. MITRE research highlights the ROOTROT webshell tool, used by attackers to execute commands, steal credentials, exfiltrate files, and more. Vulnerabilities in ICS devices are exploited to propagate the Mirai botnet, leading to large-scale DDoS attacks and other cyber threats.
Why Should TPRM Professionals Care About this Vulnerability?
For organizations utilizing Ivanti Connect Secure, this vulnerability could lead to complete system compromise. Given the privileged role these systems play in secure communications and network management, the exploitation of this flaw could result in data breaches, system disruptions, and potential ransomware attacks. Attackers could use compromised admin credentials to access and exploit this vulnerability, especially in environments where access controls are weak or multi-factor authentication (MFA) is not implemented.
What Questions Should TPRM Professionals Ask Vendors About This Vulnerability?
- Have you upgraded all instances of Ivanti Connect Secure and Policy Secure to versions 22.7R2.1, 22.7R2.2, and 22.7R1.1 respectively to mitigate the risk of CVE-2024-37404?
- Can you confirm if you have implemented the recommended mitigation measures such as enabling admin access only on the management interface, monitoring network traffic for unusual activities, and strengthening password policies and MFA protections?
- Have you taken steps to prevent the injection of Carriage Return Line Feed (CRLF) characters into input fields in the admin portal, specifically in the Certificate Signing Request (CSR) generation process, to prevent the manipulation of configuration files and loading of malicious libraries?
- Can you confirm if you have implemented measures to detect and prevent the uploading of malicious ZIP files masquerading as client logs, which could lead to remote code execution and granting of root-level access to the system?
Remediation Recommendations for Vendors Subject to This Risk
Vendors using Authentik should follow these remediation steps:
- Update to the latest versions of Ivanti Connect Secure (22.7R2.1 or 9.1R18.9 when available) and Ivanti Policy Secure (22.7R1.1).
- Restrict admin access to internal networks and ensure it is protected by a firewall or jump host.
- Enforce strong access controls, including MFA and password vaults, to limit exposure.
- Enable admin logging and monitor for suspicious activity involving administrative credentials.
How Can TPRM Professionals Leverage Black Kite for This Vulnerability?
Black Kite provides the Ivanti Connect Secure FocusTag, which helps TPRM professionals identify vendors at risk of this vulnerability. Published in October 2024, this FocusTag delivers critical insights into affected assets, allowing TPRM professionals to prioritize vendors that need immediate remediation. This targeted intelligence aids in reducing exposure by focusing on the vendors most likely to be impacted by CVE-2024-37404, helping organizations streamline their third-party risk management processes.
By providing detailed asset information such as vulnerable subdomains or IP addresses, Black Kite allows its customers to operationalize these insights and reduce the potential risk from vendors who might be compromised through this vulnerability.
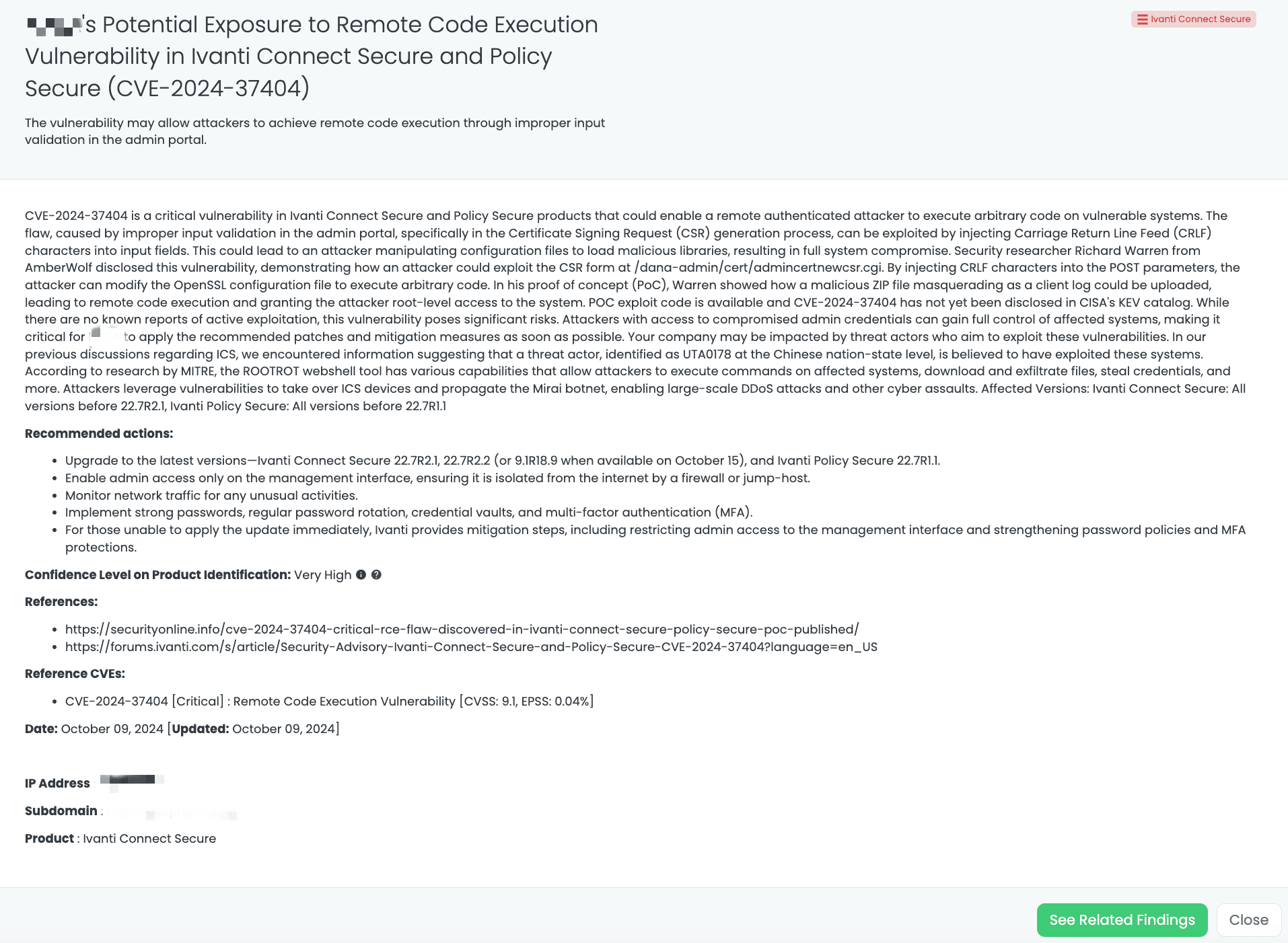
Black Kite’s Ivanti Connect Secure FocusTag™ details critical insights on the event for TPRM professionals.
Maximizing TPRM Effectiveness With Black Kite’s FocusTags™
Black Kite’s FocusTags are indispensable tools for refining Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) strategies. Here’s how Black Kite’s FocusTags™ empower organizations to effectively manage vulnerabilities like those in Fortinet Core Products, Cisco RV Routers, and Ivanti Connect Secure:
- Real-Time Risk Identification: FocusTags instantly identify vendors impacted by critical vulnerabilities, enabling organizations to react swiftly and mitigate threats before they escalate.
- Targeted Risk Prioritization: By assessing both the severity of the vulnerability and the criticality of the affected vendors, FocusTags help allocate resources efficiently to address the most pressing risks.
- Informed Vendor Engagement: These tags facilitate deeper discussions with vendors about their exposure and remediation plans, ensuring that conversations are focused and actionable.
- Comprehensive Security Enhancement: With a broad view of the threat landscape, FocusTags strengthen the overall security posture, allowing TPRM professionals to adapt their strategies to the latest cyber risks.
Incorporating Black Kite’s FocusTags into your TPRM processes ensures that your organization remains proactive and responsive to the rapidly evolving cyber threat environment, empowering you to manage third-party risks effectively and safeguard your enterprise.
About Focus Friday
Every week, we delve into the realms of critical vulnerabilities and their implications from a Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) perspective. This series is dedicated to shedding light on pressing cybersecurity threats, offering in-depth analyses, and providing actionable insights.
FocusTags™ in the Last 30 Days:
- Fortinet Core Products: CVE-2024-23113, Format String Vulnerability in FortiOS, FortiPAM, FortiProxy, and FortiWeb.
- Cisco RV Routers: CVE-2024-20393, CVE-2024-20470, Privilege Escalation and RCE Vulnerability in RV340, RV340W, RV345, and RV345P Dual WAN Gigabit VPN Routers.
- Ivanti Connect Secure: CVE-2024-37404, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in Ivanti Connect Secure & Policy Secure.
- Zimbra: CVE-2024-45519, Remote Command Execution Vulnerability in Zimbra.
- DrayTek Routers: CVE-2020-15415, Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in DrayTek Vigor Routers.
- Authentik: CVE-2024-47070, Authentication Bypass Vulnerability in Authentik.
- Octopus Deploy: CVE-2024-9194, SQL Injection Vulnerability in Octopus Server.
- pgAdmin: CVE-2024-9014, OAuth2 Authentication Vulnerability in pgAdmin.
- Keycloak: CVE-2024-8698, CVE-2024-8883, SAML Signature Validation Bypass and Session Hijacking Vulnerability in Keycloak.
- Navidrome: CVE-2024-47062, SQL Injection Vulnerability in Navidrome.
- PAN-OS Cleartext: CVE-2024-8687, Cleartext Exposure Security Flaw in PAN-OS, GlobalProtect, Prisma Access.
- FileCatalyst Workflow: CVE-2024-6633, CVE-2024-6632, Insecure Default Configuration and SQL Injection Vulnerability in Fortra FileCatalyst Workflow.
- WPML: CVE-2024-6386, Critical Remote Code Execution Vulnerability via Twig Server-Side Template Injection in WPML Plugin
- SonicWall Firewalls: CVE-2024-40766, Critical Improper Access Control Vulnerability in SonicWall Firewalls
- Dahua IP Camera: CVE-2021-33045, CVE-2021-33044, Critical Authentication Bypass Vulnerabilities in Dahua IP Camera Systems
- Microsoft Privilege Escalation Vulnerability: CVE-2024-38193, CVE-2024-38106, CVE-2024-38107, Critical Privilege Escalation Vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows
- SolarWinds WHD: CVE-2024-28986, Critical Remote Code Execution Vulnerability in SolarWinds Web Help Desk
References
https://www.fortiguard.com/psirt/FG-IR-24-029
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-23113